2023-06-13 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
◆リュウ氏の研究は、紫外線と亜硫酸塩を使用して塩素と炭素の結合を切断し、炭素とフッ素の結合を切断する連鎖的な化学反応を引き起こします。これにより、PFAS化合物のほぼ完全な除フルオロ化が可能になります。彼らの研究は、PFAS汚染の浄化に向けた努力において重要な成果を示しており、産業界からも注目を浴びています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2023/06/13/process-turns-harmful-pollutants-harmless-substances
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44221-023-00046-z
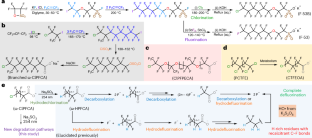
塩素化ポリフルオロアルキル物質の光化学分解経路とほぼ完全な脱フルオロ化 Photochemical degradation pathways and near-complete defluorination of chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl substances
Jinyu Gao,Zekun Liu,Zhanghao Chen,Dandan Rao,Shun Che,Cheng Gu,Yujie Men,Jun Huang & Jinyong Liu
Nature Water Published:03 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-023-00046-z
Abstract
Chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl substances (Clx–PFAS) are an emerging class of pollutants worldwide. Here we demonstrate near-complete defluorination (that is, cleaving most C–F bonds) of diverse Clx–PFAS structures and the reaction mechanisms. First, we used ultraviolet/sulfite to degrade various carboxylic acids (n = 1, 2, 4 and 8 Cl–CnF2nCOO− and n = 1, 2 and 3 Cl–(CF2CFCl)nCF2COO−) and an ether sulfonic acid surfactant (F-53B, Cl–(CF2)6–O–(CF2)2SO3−). The initial reaction with a hydrated electron cleaved the C–Cl bond. The resulting fluorocarbon radicals (•CF2– on the terminal and –•CF– in the middle) yield C–H or C–SO3−, or form a dimer. In particular, we identified a novel reaction pathway with the unexpected HO• radical to cleave the C–C bond (for –•CF–) and yield –COO−. This pathway is critical for rapid and deep defluorination at 90–96% from carboxylic acids and 76% from F-53B. The following treatment with heat/persulfate at pH >12 achieved ~100% overall defluorination from carboxylic acids and 93% from F-53B without producing toxic ClO3− from Cl−. This study advances the understanding of PFAS transformation in engineering systems. It also suggests a synergy between molecular design and degradation technology towards sustainable management of fluorochemicals.