2023-03-21 パデュー大学
この研究は、Nature Portfolioが発行する査読付きオープンアクセス科学雑誌「Nature Communications」2月10日号に掲載されました。
ViPERグループは、次世代の安全なリチウムイオン、リチウム硫黄、ナトリウムイオン、固体、超低温電池システム用の高容量材料の設計と製造に重点を置いています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/releases/2023/Q1/purdues-viper-group-innovates-high-energy-density,-long-life-cycle-rechargeable-litium-metal-batteries.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-36647-1
高電圧安定型非水系リチウム金属電池用非極性エーテル系電解質溶液 Non-polar ether-based electrolyte solutions for stable high-voltage non-aqueous lithium metal batteries
Zheng Li,Harsha Rao,Rasha Atwi,Bhuvaneswari M. Sivakumar,Bharat Gwalani,Scott Gray,Kee Sung Han,Thomas A. Everett,Tanvi A. Ajantiwalay,Vijayakumar Murugesan,Nav Nidhi Rajput & Vilas G. Pol
Nature Communications Published:16 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36647-1
Abstract
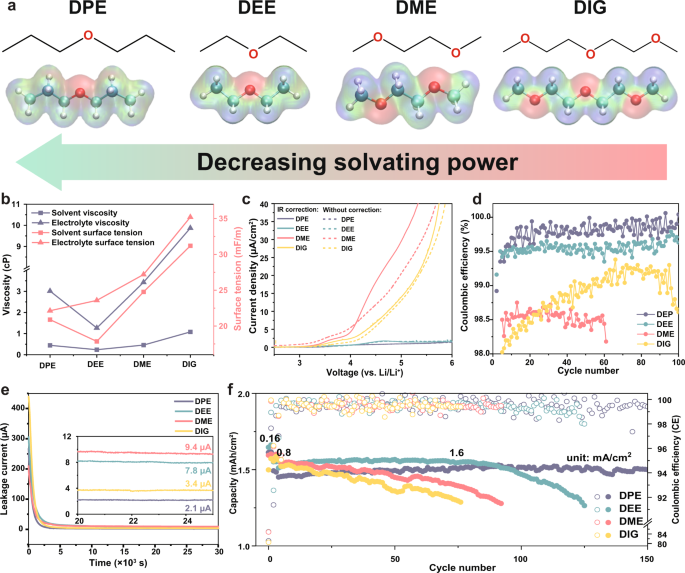
The electrochemical instability of ether-based electrolyte solutions hinders their practical applications in high-voltage Li metal batteries. To circumvent this issue, here, we propose a dilution strategy to lose the Li+/solvent interaction and use the dilute non-aqueous electrolyte solution in high-voltage lithium metal batteries. We demonstrate that in a non-polar dipropyl ether (DPE)-based electrolyte solution with lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl) imide salt, the decomposition order of solvated species can be adjusted to promote the Li+/salt-derived anion clusters decomposition over free ether solvent molecules. This selective mechanism favors the formation of a robust cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI) and a solvent-deficient electric double-layer structure at the positive electrode interface. When the DPE-based electrolyte is tested in combination with a Li metal negative electrode (50 μm thick) and a LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2-based positive electrode (3.3 mAh/cm2) in pouch cell configuration at 25 °C, a specific discharge capacity retention of about 74% after 150 cycles (0.33 and 1 mA/cm2 charge and discharge, respectively) is obtained.