2025-11-05 オーストラリア連邦・テクノロジー・シドニー大学 (UTS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.uts.edu.au/news/2025/11/scientists-reveal-it-is-possible-to-beam-up-quantum-signals
- https://journals.aps.org/prresearch/abstract/10.1103/v3p1-kz4h
アップリンク衛星チャネルを介した量子もつれ配信 Quantum entanglement distribution via uplink satellite channels
S. Srikara, Hudson Leone, Alexander S. Solntsev, and Simon J. Devitt
Physical Review Research Published: 14 October, 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/v3p1-kz4h
Abstract
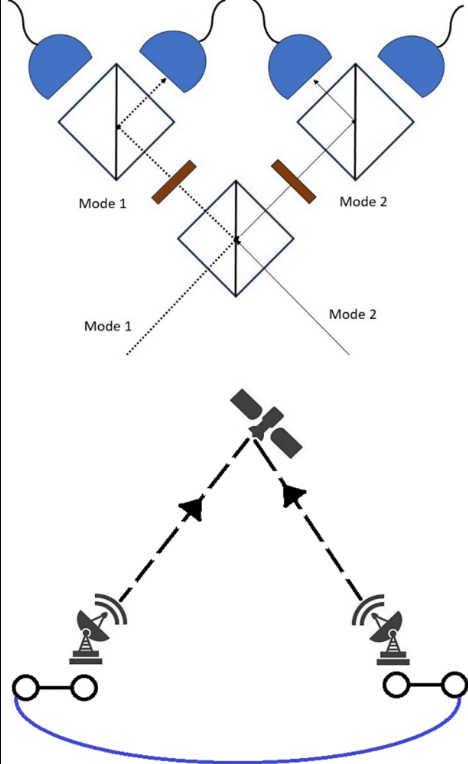
Significant work has been done to develop quantum satellites, which generate entangled pairs in space and distribute them to ground stations separated some distance away. The reverse “uplink” case, where pairs are generated on the ground and swapped on the satellite using an optical Bell measurement, has not been seriously considered due to a prevailing assumption that it is practically infeasible. In this paper, we illustrate the feasibility of performing Discrete Variable photonic Bell measurements in space by conducting a detailed numerical analysis to estimate the channel efficiency and attainable pair fidelity for various satellite-station configurations. Our model accounts for a wide range of physical effects such as atmospheric effects, stray photons, and mode mismatch. Our findings show promise toward the feasibility of photonic Bell measurements in space, which motivates future research toward large-scale satellite-based uplink entanglement distribution.