2026-01-09 東京科学大学
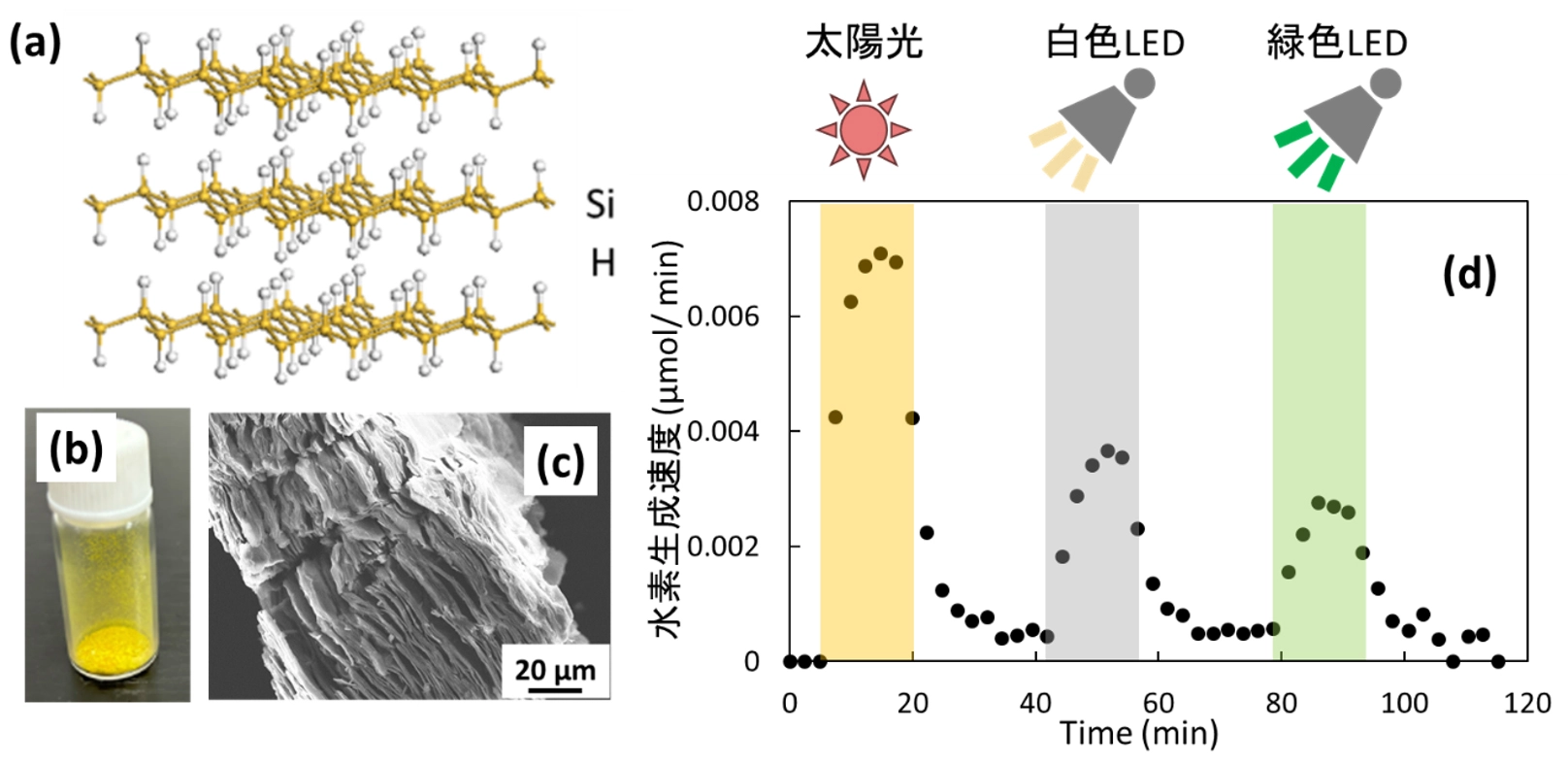
図1. 層状水素化シリカンの結晶構造(a)、粉末の写真(b)、走査型電子顕微鏡像(c)、可視光による水素放出特性(d)。可視光は疑似太陽光、白色LED、緑色LEDを用いた。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/u1ttc2gkmh7l
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2910&prevId=&key=4477b080862d2f99610530d8fd19cdd8.pdf
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adom.202502880
層状水素シリカからの可視光駆動型水素放出 Visible-Light-Driven Hydrogen Release from Layered Hydrogen Silicane
Hirona Ito, Mio Nakai, Akira Yamaguchi, Shin-ichi Ito, Osamu Oki, Takahiro Kondo, Masahiro Miyauchi, Hideyuki Nakano
Advanced Optical Materials Published: 29 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202502880
Abstract
To use solar energy effectively, environmentally benign solid-state hydrogen storage materials are sought that are capable of releasing hydrogen under visible light irradiation. The gravimetric hydrogen capacity of layered hydrogen silicane (L-HSi) is quite high (3.44 wt.%). The optical bandgap of L-HSi is 2.13 eV, which corresponds to a wavelength of ≈600 nm (green-to-yellow region). Here, visible-light-driven hydrogen release from L-HSi is reported. The action spectrum of L-HSi for hydrogen release is consistent with its absorption spectrum, indicating that hydrogen release is driven by bandgap excitation rather than the photothermal effect. The quantum efficiency of hydrogen release is 7.3% at 550 nm. Hydrogen release from L-HSi can occur under both inert gas conditions and in the dispersed liquid form. The light intensity dependence indicates that hydrogen release is driven by low-intensity light such as sunlight or a light-emitting diode. L-HSi is expected to be used as a safe, solid-state, and lightweight hydrogen carrier with low energy consumption for hydrogen release.