2025-12-01 アリゾナ大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.arizona.edu/news/newly-discovered-star-opens-laboratory-solving-cosmic-dust-mystery
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-3881/adfe66
ホットダストシステムκTuc Aのサブコンポーネントの干渉検出と軌道モデリング:階層的五重星系における偏心軌道上の低質量星 Interferometric Detection and Orbit Modeling of the Subcomponent in the Hot-dust System κ Tuc A: A Low-mass Star on an Eccentric Orbit in a Hierarchical-quintuple System
T. A. Stuber, A. Mérand, F. Kirchschlager, S. Wolf, G. Weible, O. Absil, T. D. Pearce, G. Garreau, J.-C. Augereau, W. C. Danchi,…
The Astronomical Journal Published: 2025 December 1
DOI:10.3847/1538-3881/adfe66
Abstract
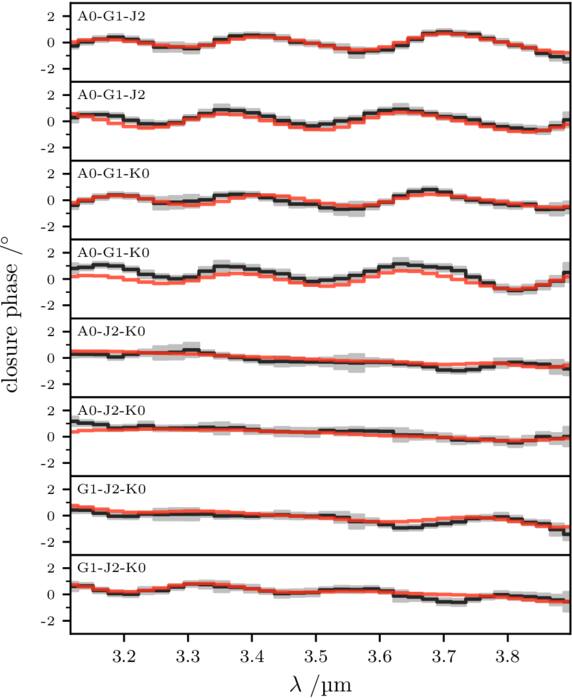
The system κ Tuc A is part of a hierarchical-quintuple system and is a prime target for studies of hot-exozodiacal dust, because a time-variable near-infrared excess has been detected. We observed the system with the Multi Aperture mid-Infrared Spectroscopic Experiment (MATISSE) and GRAVITY at the Very Large Telescope Interferometer, and detected the stellar companion to the primary κ Tuc Aa that was previously inferred by astrometry, κ Tuc Ab. Its L-band flux ratio to the primary is 1.32% and its signature in the MATISSE closure phases is mostly smaller than ±2°, which makes κ Tuc Ab the highest-contrast companion ever detected with MATISSE closure phases. We verified with GRAVITY that relative astrometry with milliarcsecond precision can be retrieved from MATISSE closure phases. Using multiple epochs of observations, we obtain a full orbital solution for κ Tuc Ab. Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.94 and a semimajor axis of 4.8 au. The orbit of κ Tuc Ab and the orbit of the wider separation companion κ Tuc B are mutually inclined. Based on the measured flux ratio of κ Tuc Ab to Aa and their dynamical mass, we estimate the spectral type of κ Tuc Ab to be M3.5 V to M4.5 V. While the then unknown star κ Tuc Ab might have caused the putative detection of hot-exozodiacal dust around κ Tuc Aa in 2012 and 2014, this cannot be for the detection in 2019, giving rise to an intriguing system architecture. This motivates studies investigating the interplay of the low-mass star on an eccentric orbit, the hot-exozodiacal dust, and a possible planetesimal reservoir.