2025-09-25 大阪大学
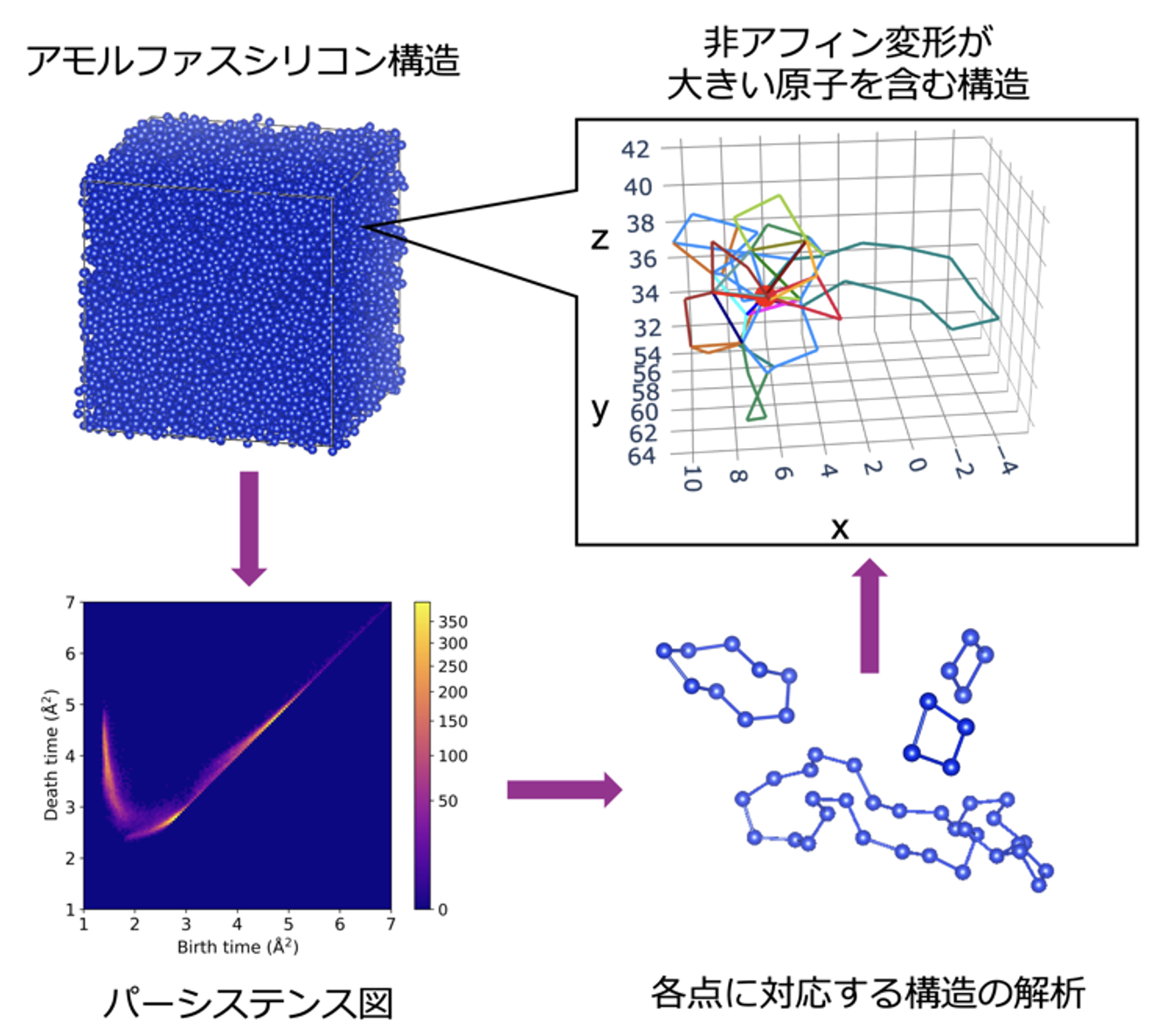
図1 本研究成果のまとめ。アモルファスシリコンの構造から得られたパーシステンス図と、その中の各点に対応する構造の例、および非アフィン変形が大きい原子を含む構造の代表例
<関連情報>
- https://www.sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp/achievement/release/20250925.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63424-z
持続的相同性は共有結合性非晶質固体の機械的性質に関与する階層構造を解明する Persistent homology elucidates hierarchical structures responsible for mechanical properties in covalent amorphous solids
Emi Minamitani,Takenobu Nakamura,Ippei Obayashi & Hideyuki Mizuno
Nature Communications Published:25 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-63424-z
Abstract
Understanding how atomic-level structures govern the mechanical properties of amorphous materials remains a fundamental challenge in solid-state physics. Under mechanical loading, amorphous materials exhibit simple affine and spatially inhomogeneous nonaffine displacements that contribute to the elastic modulus through the Born (affine) and nonaffine terms, respectively. The differences between soft local structures characterized by small Born terms or large nonaffine displacements have yet to be elucidated. This challenge is particularly complex in covalent amorphous materials such as silicon, where the medium-range order (MRO) plays a crucial role in the network structure. To address these issues, we combined molecular dynamics simulations with persistent homology analysis. Our results reveal that local structures with small Born terms are governed by short-range characteristics, whereas those with large nonaffine displacements exhibit hierarchical structures in which short-range disorder is embedded within the MRO. These hierarchical structures are also strongly correlated with low-energy localized vibrational excitations. Our findings demonstrate that the mechanical responses and dynamic properties of covalent amorphous materials are intrinsically linked to the MRO, providing a framework for understanding and tailoring their properties.