2025-08-26 北京大学(PKU)
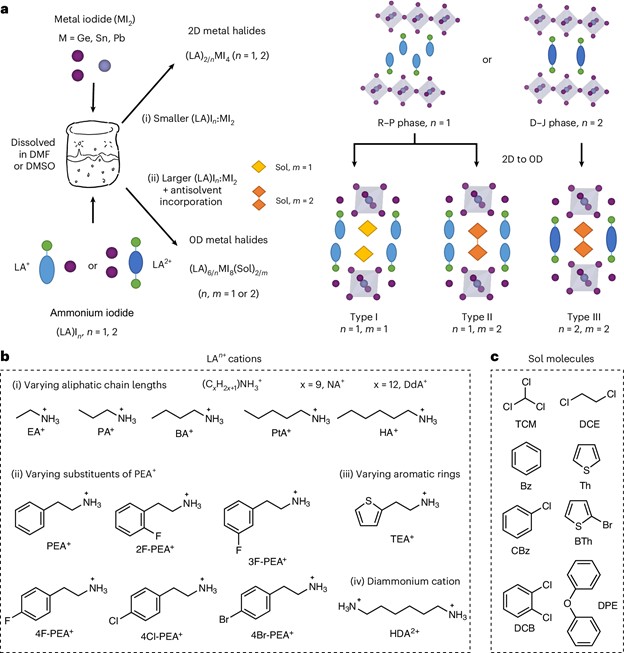
Figure 1. Solvent-embedding synthesis route transforming 2D halides into 0D metal iodides.
<関連情報>
- https://newsen.pku.edu.cn/news_events/news/research/15066.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01869-x
溶媒取り込みによるゼロ次元八面体金属ハロゲン化物の合成とその光物理特性 Synthesis of zero-dimensional octahedral metal halides through solvent incorporation and their photophysical properties
Nanlong Zheng,Songqi Cao,Tianhao Zhang,Peihao Huo,Conglan Hu,Huanyu Liu,Ruoyao Guo,Wenchao Yan,Jiayin Zheng,Xiaofan Jiang,Zhenyu Zhu,Junliang Sun,Hong Jiang,Zuqiang Bian,Yongping Fu & Zhiwei Liu
Nature Chemistry Published:04 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-025-01869-x
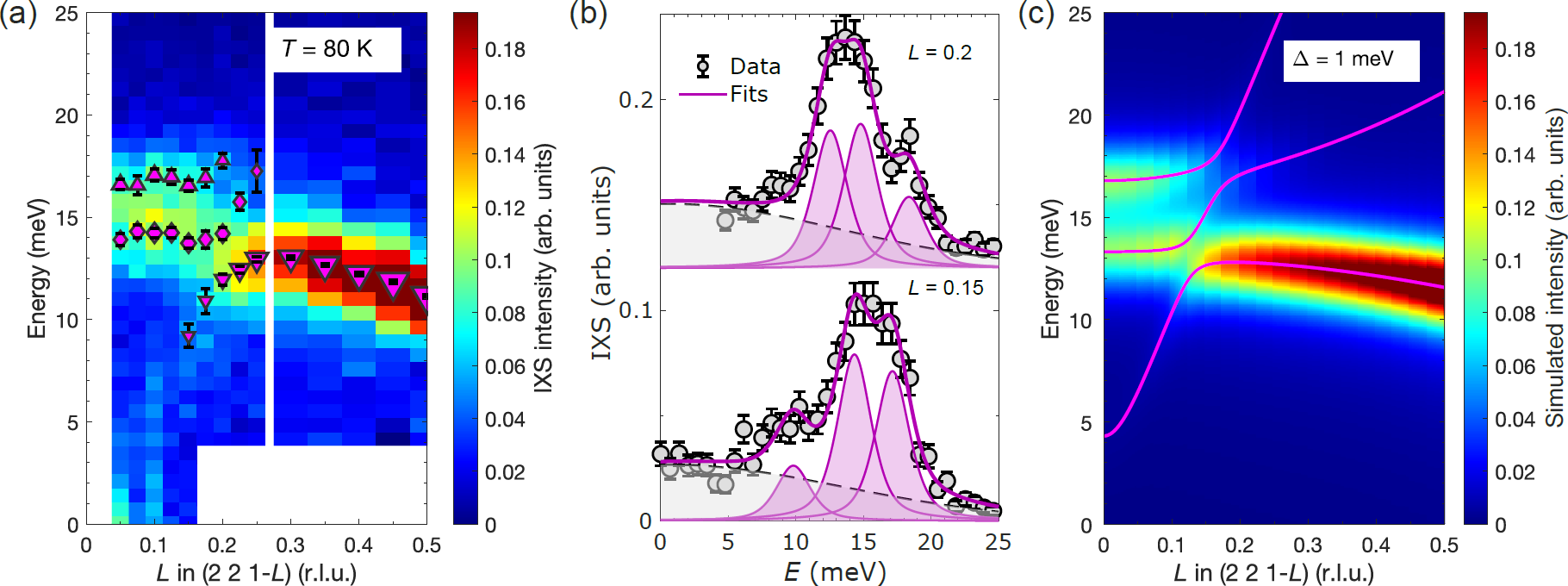
Abstract
Zero-dimensional (0D) metal halides, which feature discrete metal halide octahedra interspersed with large organoammonium cations, are the building blocks of halide perovskites. The optical properties of these materials make them promising candidates in light-emitting devices. However, developing their general design principles remains challenging. Here we report an antisolvent incorporation approach that transforms a broad range of two-dimensional tin iodide perovskites into 0D structures. This approach accommodates diverse organic cations and antisolvent molecules and is extendable to germanium and lead analogues. We show that enhancing the structural rigidity in Sn-based octahedra—modulated by organic packing—increases the radiative recombination rate while decreasing the non-radiative recombination rate, achieving near-unity photoluminescence quantum yield. Ge- and Sn-based structures exhibit large Stokes shifts and microsecond-scale triplet lifetimes due to localized excited states, while their Pb-based counterpart shows faster recombination via triplet–singlet mixing, supported by theoretical calculations. This work offers a versatile synthetic platform for 0D metal halides and deepens our current understanding of excited-state dynamics in halide perovskites.