2025-09-03 清華大学
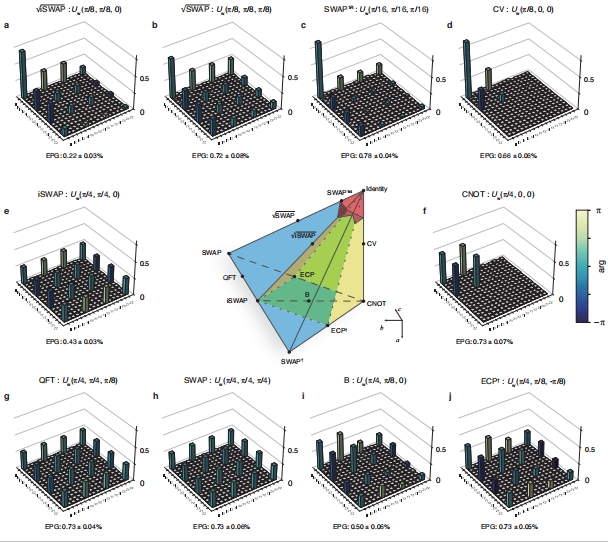
The effect of implementing common two-qubit gates such as CNOT, iSWAP, and B with AshN instruction microarchitecture.
<関連情報>
- https://www.tsinghua.edu.cn/en/info/1245/14468.htm
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-025-02990-x
- https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3620665.3640386
統一制御を用いた任意の2量子ビットゲートの高効率実装 Efficient implementation of arbitrary two-qubit gates using unified control
Zhen Chen,Weiyang Liu,Yanjun Ma,Weijie Sun,Ruixia Wang,He Wang,Huikai Xu,Guangming Xue,Haisheng Yan,Zhen Yang,Jiayu Ding,Yang Gao,Feiyu Li,Yujia Zhang,Zikang Zhang,Yirong Jin,Haifeng Yu,Jianxin Chen & Fei Yan
Nature Physics Published:15 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02990-x
Abstract
The set of quantum logic gates that can be easily implemented is fundamental to the performance of quantum computers, as it governs the accuracy of basic quantum operations and dictates the complexity of implementing quantum algorithms. Traditional approaches to extending gate sets often require operating devices outside the ideal parameter regimes used to realize qubits, leading to increased control complexity while offering only a limited set of gates. Here we experimentally demonstrate a unified and versatile gate scheme capable of generating arbitrary two-qubit gates using only an exchange interaction and qubit driving on a superconducting quantum processor. We achieve high fidelities averaging 99.38% across a wide range of commonly used two-qubit unitaries, enabling precise multipartite entangled state preparation. Furthermore, we successfully produce a B gate, which efficiently synthesizes the entire family of two-qubit gates. Our results establish that fully exploiting the capabilities of the exchange interaction can yield a comprehensive and highly accurate gate set. With maximum expressivity, optimal gate time, demonstrated high fidelity and easy adaption to other quantum platforms, our unified control scheme offers the prospect of improved performance in quantum hardware and algorithm development.
すべてを支配する単一ゲート方式:量子計算のための複雑でありながら簡素化された命令セットの導入 One Gate Scheme to Rule Them All: Introducing a Complex Yet Reduced Instruction Set for Quantum Computing
Jianxin Chen, Dawei Ding, Weiyuan Gong, Cupjin Huang, Qi Ye
ASPLOS ’24: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems Published: 27 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1145/3620665.3640386
Abstract
The design and architecture of a quantum instruction set are paramount to the performance of a quantum computer. This work introduces a gate scheme for qubits with XX + YY coupling that directly and efficiently realizes any two-qubit gate up to single-qubit gates. First, this scheme enables high-fidelity execution of quantum operations, especially when decoherence is the primary error source. Second, since the scheme spans the entire SU(4) group of two-qubit gates, we can use it to attain the optimal two-qubit gate count for algorithm implementation. These two advantages in synergy give rise to a quantum Complex yet Reduced Instruction Set Computer (CRISC). Though the gate scheme is compact, it supports a comprehensive array of quantum operations. This may seem paradoxical but is realizable due to the fundamental differences between quantum and classical computer architectures.
Using our gate scheme, we observe marked improvements across various applications, including generic n-qubit gate synthesis, quantum volume, and qubit routing. Furthermore, the proposed scheme also realizes a gate locally equivalent to the commonly used CNOT gate with a gate time of π/2g, where g is the two-qubit coupling. The AshN scheme is also completely impervious to ZZ error, the main coherent error in transversely coupled systems, as the control parameters implementing the gates can be easily adjusted to take the ZZ term into account.