2025-08-12 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
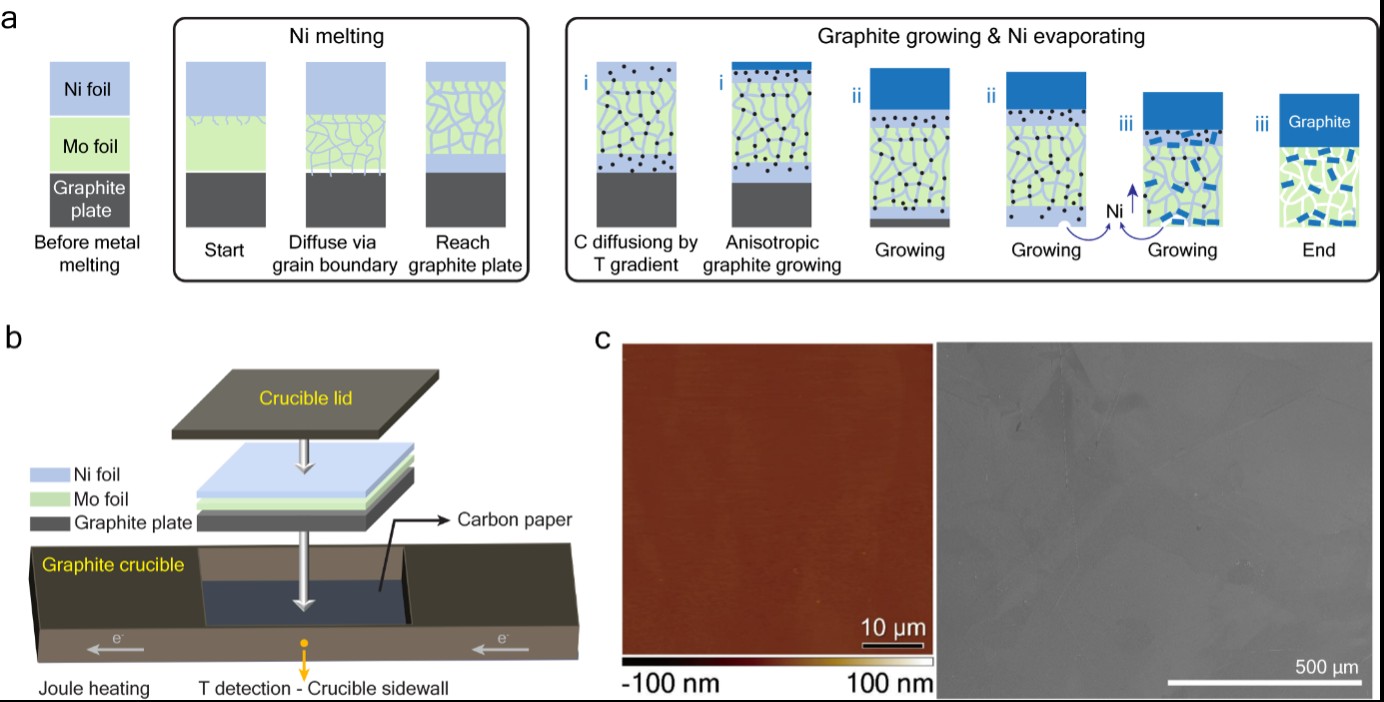
Figure 1. (a) Schematic of the suggested reaction pathway. (b) Schematic of the experimental configuration. (c) AFM height image and SEM image of the mirror-like graphite film.
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=26053&pageIndex=1&searchCnd=&searchWrd=#
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-62227-6
鏡面状の大型粒状グラファイト薄膜の合成と特性 Synthesis and properties of mirror-like large-grain graphite films
Liyuan Zhang,Meihui Wang,Dongho Jeon,Yongqiang Meng,Sun Hwa Lee,Myeonggi Choe,Yunqing Li,Mengran Wang,Sherilyn J. Lu,Zonghoon Lee,Won Kyung Seong & Rodney S. Ruoff
Nature Communications Published:12 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-62227-6
Abstract
Graphite films with large grain sizes have been reportedly obtained by using metal as catalysts, but the obtained graphite is mostly heavily wrinkled, thus containing defects that degrade its properties. We report the synthesis of mirror-like and large-grained graphite films with only a few nano kinks and controllable dimensions, achieved by using flat Ni-Mo alloy melts of the same lateral dimensions as the metal foils used to make this alloy melt. The graphite film exhibited few nano kinks and a mirror-like appearance because the deliberate evaporation of much of the Ni produced a porous substrate, which in turn dramatically weakened the substrate-graphite film interaction before cooling. The mirror-like graphite appears to be 100% AB-stacked with millimeter-sized grains that are much larger than the multi-micron grain size of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite and rivaled in size only by a small percentage of natural graphite. Our graphite films have an electrical conductivity of 2.25 × 104 S cm−1 at 300 K. Tensile loading of macroscale samples showed an average Young’s modulus of 969 ± 69 GPa and average fracture strength of 1.29 ± 0.203 GPa, and Frequency Domain Thermoreflectance revealed an average in-plane thermal conductivity of 2034.4 ± 68 W m−1·K−1.



