2025-03-10 アリゾナ大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.arizona.edu/news/james-webb-space-telescope-reveals-unexpected-complex-chemistry-primordial-galaxy
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-025-02503-z
- https://tiisys.com/blog/2024/05/31/post-138371/
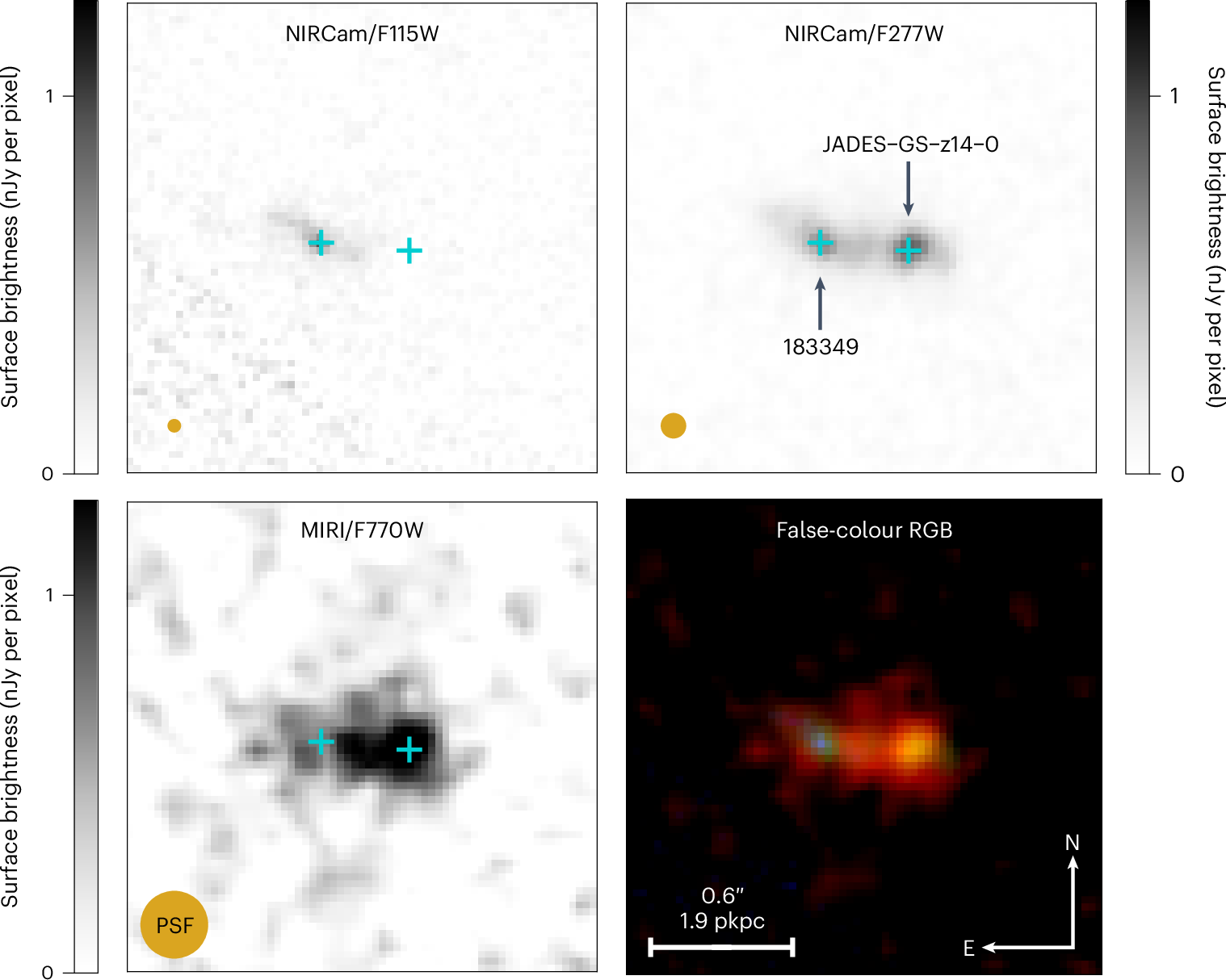
JWST/MIRIによる赤方偏移14を超える銀河の7.7μmでの測光検出 Photometric detection at 7.7 μm of a galaxy beyond redshift 14 with JWST/MIRI
Jakob M. Helton,George H. Rieke,Stacey Alberts,Zihao Wu,Daniel J. Eisenstein,Kevin N. Hainline,Stefano Carniani,Zhiyuan Ji,William M. Baker,Rachana Bhatawdekar,Andrew J. Bunker,Phillip A. Cargile,Stéphane Charlot,Jacopo Chevallard,Francesco D’Eugenio,Eiichi Egami,Benjamin D. Johnson,Gareth C. Jones,Jianwei Lyu,Roberto Maiolino,Pablo G. Pérez-González,Marcia J. Rieke,Brant Robertson,Aayush Saxena,… Yongda Zhu
Nature Astronomy Published:07 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-025-02503-z
Abstract
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has spectroscopically confirmed numerous galaxies at z > 10. While weak rest-frame ultraviolet emission lines have only been seen in a handful of sources, the stronger rest-frame optical emission lines are highly diagnostic and accessible at mid-infrared wavelengths with the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) of JWST. We report the photometric detection of the distant spectroscopically confirmed galaxy JADES-GS-z14-0 at z=14.32+0.08−0.20 with MIRI at 7.7 μm. The most plausible solution for the stellar-population properties is that this galaxy contains half a billion solar masses in stars with a strong burst of star formation in the most recent few million years. For this model, at least one-third of the flux at 7.7 μm originates from the rest-frame optical emission lines Hβ and/or [O iii]λλ4959, 5007. The inferred properties of JADES-GS-z14-0 suggest rapid mass assembly and metal enrichment during the earliest phases of galaxy formation. This work demonstrates the unique power of mid-infrared observations in understanding galaxies at the redshift frontier.



