2023-06-12 カリフォルニア工科大学(Caltech)
◆カリフォルニア工科大学のZTFが最初に発見し、その明るさが通常よりも明るかったことから強い重力レンズ効果と判明しました。これにより、銀河の内核の物質量と分布を研究する上で重要な情報が得られます。
<関連情報>
- https://www.caltech.edu/about/news/astronomers-discover-extremely-warped-supernova
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41550-023-01981-3
拡大された標準キャンドルSNズウィッキーで重力レンズ銀河の集団を発見 Uncovering a population of gravitational lens galaxies with magnified standard candle SN Zwicky
Ariel Goobar,Joel Johansson,Steve Schulze,Nikki Arendse,Ana Sagués Carracedo,Suhail Dhawan,Edvard Mörtsell,Christoffer Fremling,Lin Yan,Daniel Perley,Jesper Sollerman,Rémy Joseph,K-Ryan Hinds,William Meynardie,Igor Andreoni,Eric Bellm,Josh Bloom,Thomas E. Collett,Andrew Drake,Matthew Graham,Mansi Kasliwal,Shri R. Kulkarni,Cameron Lemon,Adam A. Miller,James D. Neill,Jakob Nordin,Justin Pierel,Johan Richard,Reed Riddle,Mickael Rigault,Ben Rusholme,Yashvi Sharma,Robert Stein,Gabrielle Stewart,Alice Townsend,Yozsef Vinko,J. Craig Wheeler & Avery Wold
Nature Astronomy Published:12 June 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-023-01981-3
Abstract
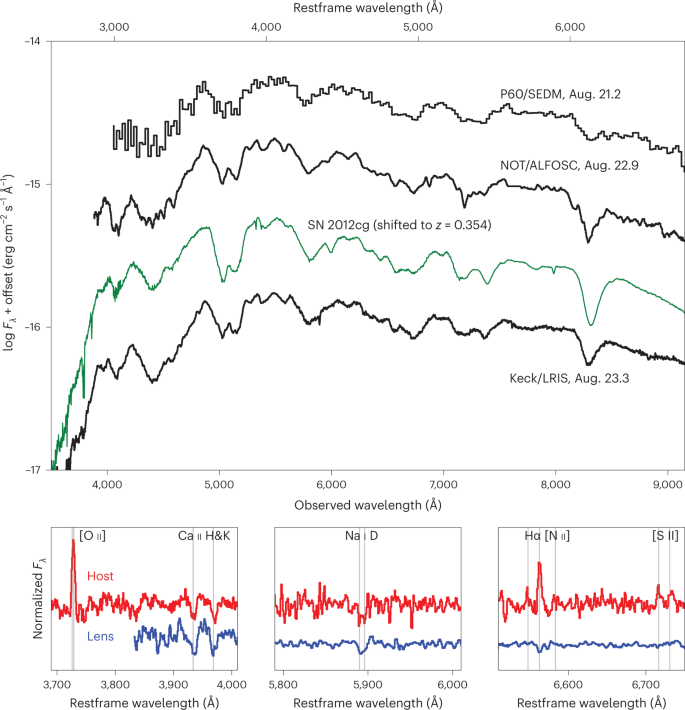
Detecting gravitationally lensed supernovae is among the biggest challenges in astronomy. It involves a combination of two very rare phenomena: catching the transient signal of a stellar explosion in a distant galaxy and observing it through a nearly perfectly aligned foreground galaxy that deflects light towards the observer. Here we describe how high-cadence optical observations with the Zwicky Transient Facility, with its unparalleled large field of view, led to the detection of a multiply imaged type Ia supernova, SN Zwicky, also known as SN 2022qmx. Magnified nearly 25-fold, the system was found thanks to the standard candle nature of type Ia supernovae. High-spatial-resolution imaging with the Keck telescope resolved four images of the supernova with very small angular separation, corresponding to an Einstein radius of only θE = 0.167″ and almost identical arrival times. The small θE and faintness of the lensing galaxy are very unusual, highlighting the importance of supernovae to fully characterize the properties of galaxy-scale gravitational lenses, including the impact of galaxy substructures.