2026-02-17 北海道大学
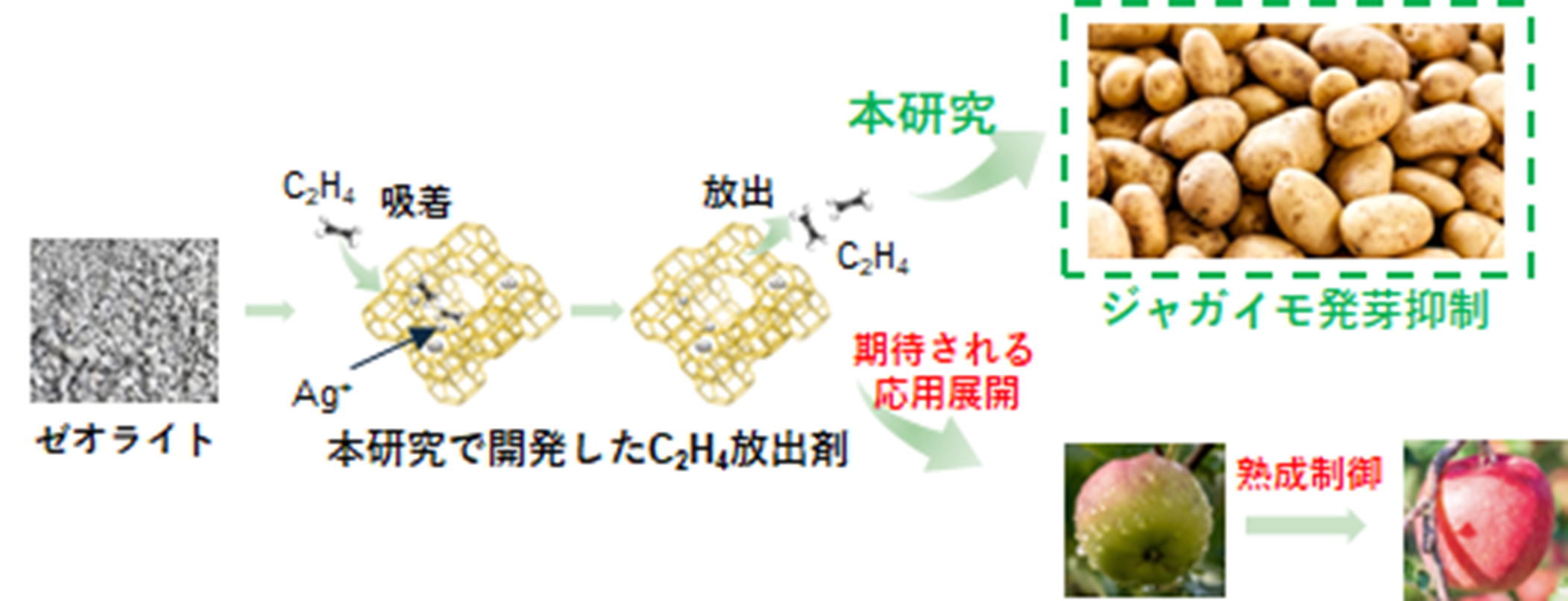
本研究の概要図
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2026/02/post-2189.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/260217_pr.pdf
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2026/gc/d5gc05933j
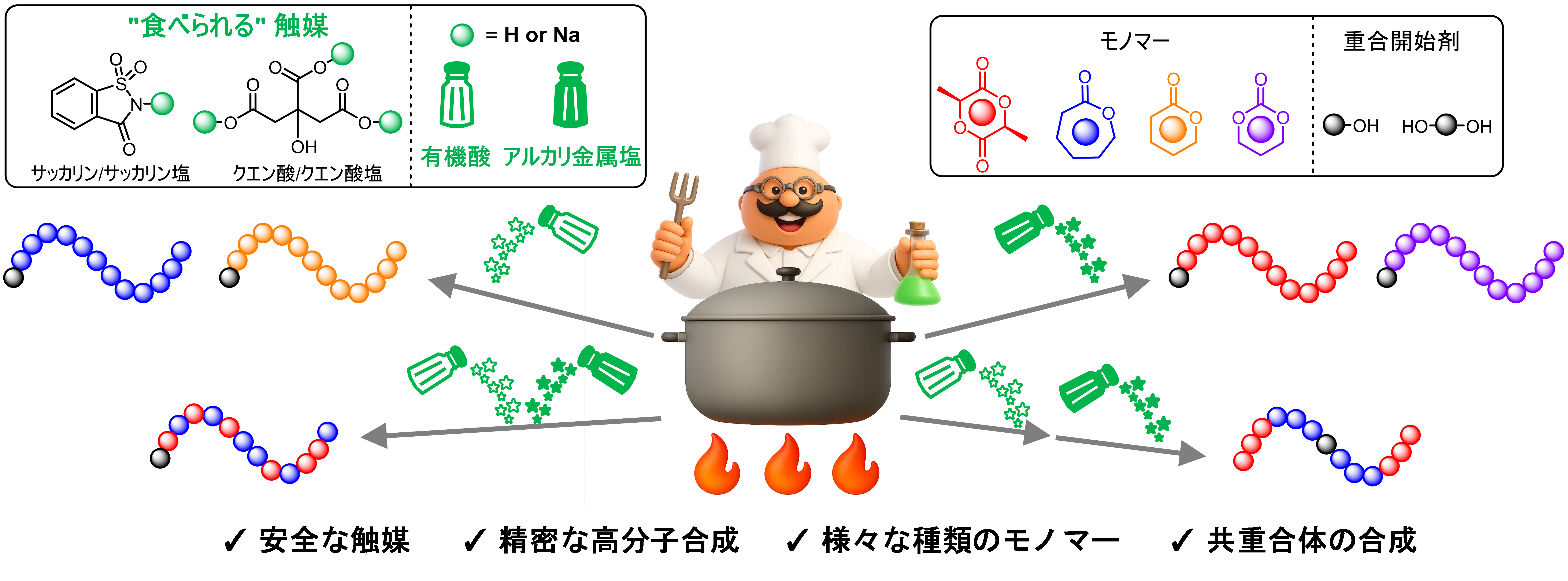
食べられる触媒を用いた生分解性ポリエステルの精密合成 Well-controlled synthesis of biodegradable polyesters using edible catalysts
Toshiki Miwa,Ryota Suzuki,Tianle Gao,Takuya Yamamoto, Feng Li,Takuya Isono and Toshifumi Satoh
Green Chemistry Published:02 Feb 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D5GC05933J
Abstract
Biodegradable polyesters, represented by polylactic acid and poly(ε-caprolactone), are regarded as not only environmentally friendly alternatives to current nondegradable polyolefins but also important polymer materials for biomedical applications. The ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of the corresponding cyclic esters is a typical approach for synthesizing these polyesters in a well-controlled and efficient manner. A wide variety of organometallics and organocatalysts have been developed for this polymerization process. Organocatalysts are considered safer than organometallic catalysts because they do not release toxic metal residues, but not all of them are necessarily harmless to humans or the environment. Some truly safe and edible catalysts, including sodium acetate and vitamin C, have been reported to catalyze the ROP of lactide or ε-caprolactone. In this study, we explore the concept of “edible catalysts” by screening the structures of various organic acids and their sodium or potassium salts as catalysts for the ROP of cyclic esters. We demonstrate the suitability of various edible compounds for different cyclic ester monomers. The synthesized polyesters had a relatively narrow dispersity (Đ = 1.1–1.3) with a well-controlled polymer chain-end structure, identical to those obtained using conventional catalysts. Moreover, by mixing different edible catalysts, random and block copolymers can be synthesized in a well-controlled manner. These findings demonstrate that unassuming edible compounds in our daily lives possess significant potential as safe and effective catalysts for the synthesis of biodegradable polymer materials.