2026-01-26 日本原子力研究開発機構,福井大学,東京科学大学,量子科学技術研究開発機構
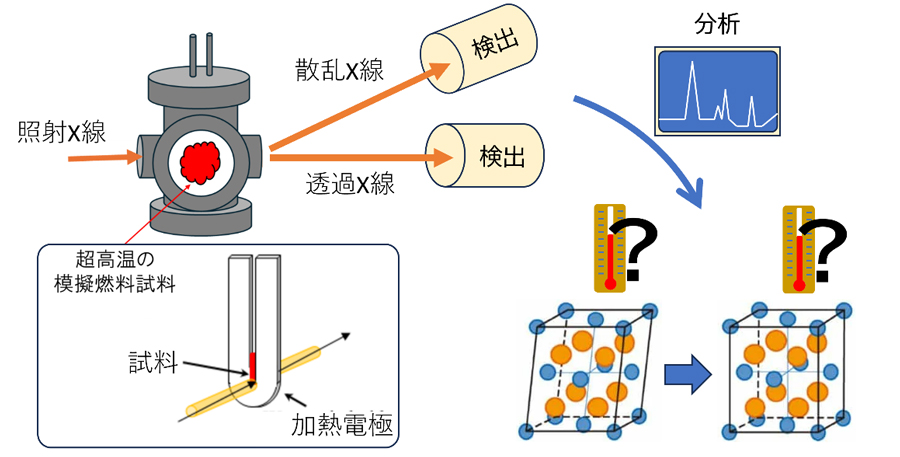
高温環境での実験をリアルタイムに分析できる装置の概念図
<関連情報>
- https://www.jaea.go.jp/02/press2025/p26012601/
- https://academic.oup.com/bcsj/article/98/10/uoaf088/8255950
超高温金属酸化物のその場迅速X線吸収微細構造とX線回折システムの組み合わせ Combined in situ quick X-ray absorption fine structure and X-ray diffraction systems for ultra-high temperature metal oxides
Hajime Tanida,Tohru Kobayashi,Tsuyoshi Yaita,Masaaki Kobata,Tatsuo Fukuda,Ayumi Itoh,Kenji Konashi,Yuji Arita
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan Published:16 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/bulcsj/uoaf088
Abstract
Structural analysis using synchrotron radiation, such as X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS), is an effective means of investigating physical properties of materials at high temperatures in order to experimentally clarify their physical properties. However, accurate temperature measurements above 2,800 K are difficult, complicating the assessment of structural changes in materials. This study addresses these issues by employing a newly developed furnace capable of reaching 2,800 K and performing in situ rapid XAFS and XRD measurements. These advances will improve our understanding of metal oxides at melting points and provide valuable insights into their behavior under extreme conditions.



