2025-12-22 エディンバラ大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.ed.ac.uk/news/shrinking-ai-memory-boosts-accuracy
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.05345
- https://openreview.net/pdf?id=8ZiElzQxf1
KVキャッシュ圧縮による推論時間ハイパースケーリング Inference-Time Hyper-Scaling with KV Cache Compression
Adrian Łańcucki, Konrad Staniszewski, Piotr Nawrot, Edoardo M. Ponti
arXiv last revised 7 Nov 2025 (this version, v2)
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2506.05345
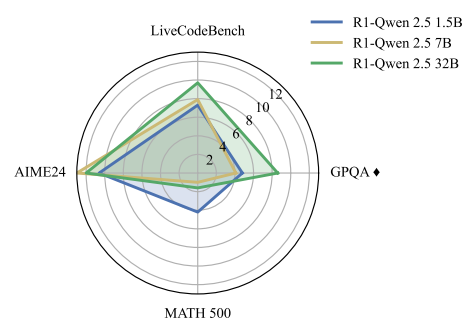
Abstract
Inference-time scaling trades efficiency for increased reasoning accuracy by generating longer or more parallel sequences. However, in Transformer LLMs, generation cost is bottlenecked by the size of the key–value (KV) cache, rather than the number of generated tokens. Hence, we explore inference-time hyper-scaling: by compressing the KV cache, we can generate more tokens within the same compute budget and further improve the accuracy of scaled inference. The success of this approach, however, hinges on the ability of compression methods to preserve accuracy even at high compression ratios. To make hyper-scaling practical, we introduce Dynamic Memory Sparsification (DMS), a novel method for sparsifying KV caches that only requires 1K training steps to achieve 8× compression, while maintaining better accuracy than training-free sparse attention. Instead of prematurely discarding cached tokens, DMS delays token eviction, implicitly merging representations and preserving critical information. We demonstrate the effectiveness of inference-time hyper-scaling with DMS on multiple families of LLMs, showing that it boosts accuracy for comparable inference latency and memory load. For instance, we enhance Qwen-R1 32B by 12.0 points on AIME 24, 8.6 on GPQA, and 9.7 on LiveCodeBench on average for an equivalent number of memory reads.



