2025-12-13 中国科学院(CAS)
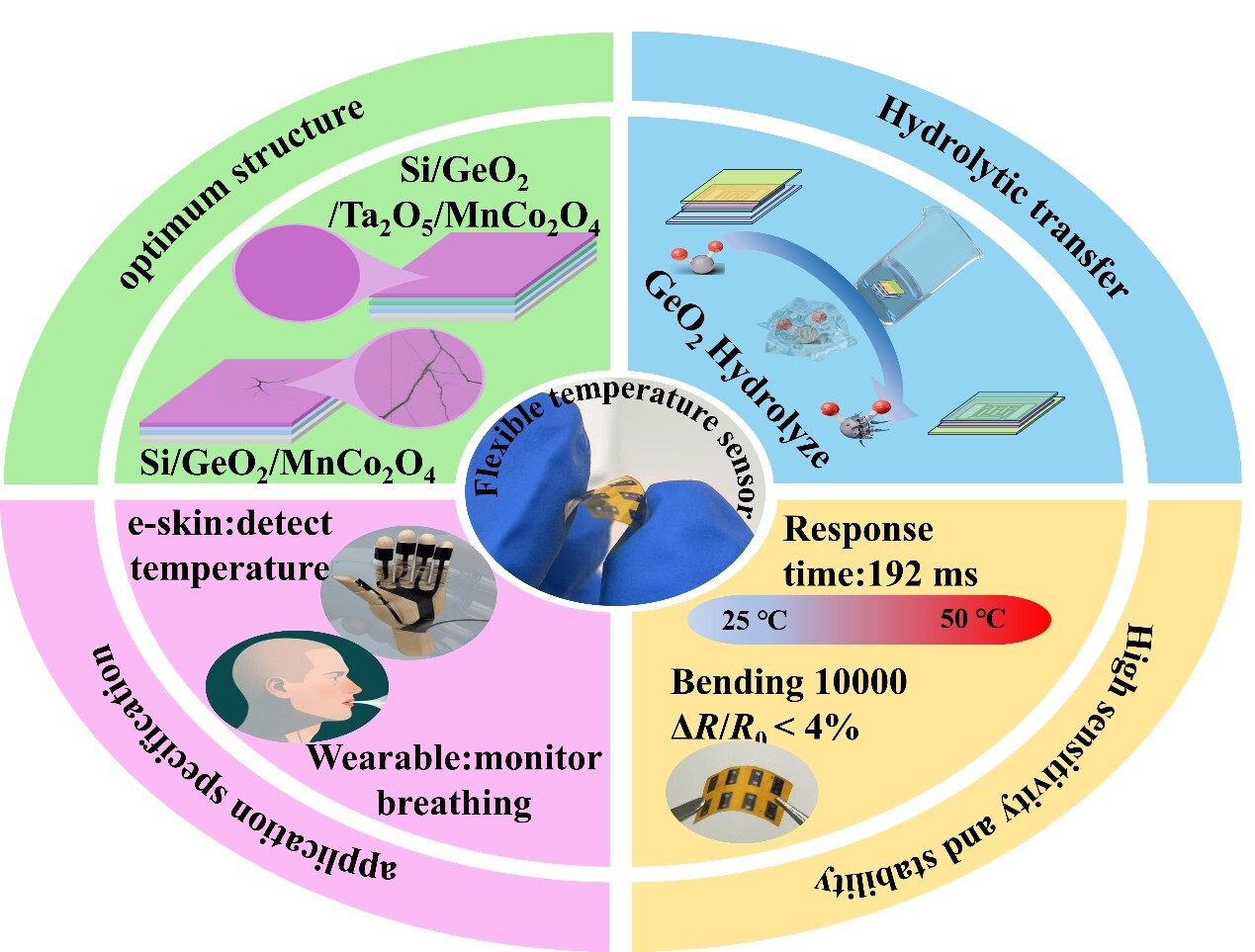
PI/MnCo2O4/Ta2O5 Flexible Temperature Sensor. (Image by YAN Xijun)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/chem/202512/t20251215_1137051.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.5c19044
極めて高い安定性を備えた高感度フレキシブル温度センサーのための水溶性GeO 2転写超薄PI/MnCo 2 O 4 /Ta 2 O 5ヘテロ構造 Water-Soluble GeO2-Transferred Ultrathin PI/MnCo2O4/Ta2O5 Heterostructures for High-Sensitivity Flexible Temperature Sensors with Extreme Stability
Xijun Yan,Yuxian Song,Xinmiao Wang,Bo Yang,Jian Wang,Yingying Dou,and Wenwen Kong
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces Published November 30, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5c19044
Abstract
Despite advancements in flexible temperature sensors, achieving high sensitivity with robust stability remains a critical challenge. In this work, we present a 40 μm-thick ultrathin, flexible negative temperature coefficient (NTC) sensor based on PI/MnCo2O4/Ta2O5, fabricated via a water-soluble GeO2 sacrificial layer transfer technique. The sensor exhibits exceptional performance, including a high temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) of −4.1%/°C, outstanding mechanical durability (ΔR < 4% after 10,000 bending cycles), and remarkable thermal stability (ΔR < 1.5% under thermal shock). The B25/50 value remains stable at 3650–3750 K, confirming excellent compositional reliability. Demonstrations in robotic e-skin and real-time respiratory monitoring highlight its potential for next-generation wearable technologies. This work provides a scalable strategy for high-performance flexible sensors in extreme environments.