2025-12-04 スウェーデン王立工科大学(KTH)
<関連情報>
- https://www.kth.se/en/om/nyheter/centrala-nyheter/alternative-to-bpa-passes-toxicity-and-sustainability-standards-set-by-eu-innovation-guidelines-1.1444641
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41893-025-01672-z
非エストロゲン性ビスフェノール由来のポリエステルに対する、安全で持続可能な設計アプローチ Safe-and-sustainable-by-design approach to polyesters from non-oestrogenic bisphenols
Cristiana Margarita,Paula Pierozan,Sathiyaraj Subramaniyan,Andrey Shatskiy,Darius Pakarinen,Annabelle Fritz,Emma Lundqvist,Victoria Chu,Hampus Hagelin,Ulf Norinder,Minna Hakkarainen,Oskar Karlsson & Helena Lundberg
Nature Sustainability Published:04 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-025-01672-z
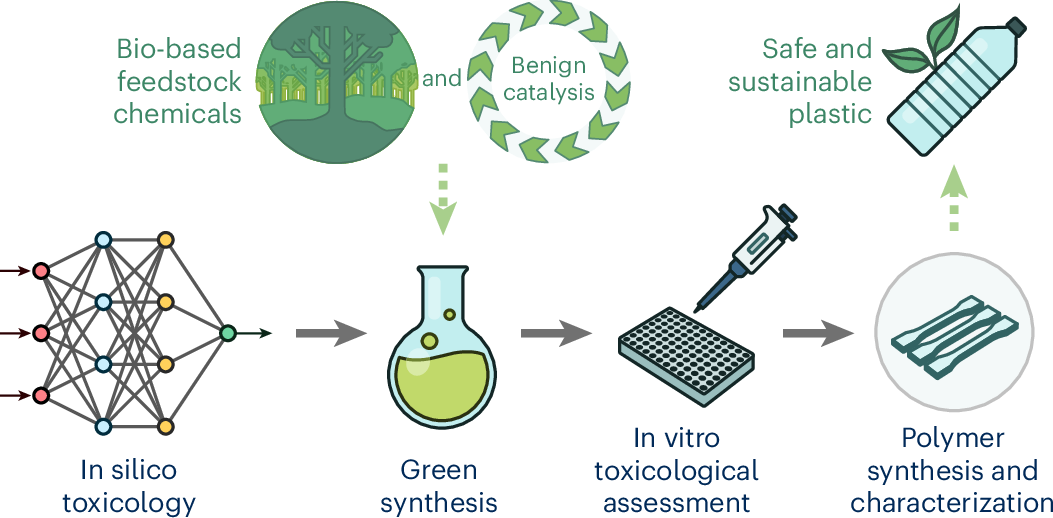
Abstract
Most contemporary chemical processes rely on non-renewable resources and reagents associated with negative impact on environment and human health. As a result, the safe-and-sustainable-by-design (SSbD) framework is launched to guide the innovation towards safe and sustainable materials and chemical products. Bisphenol A (BPA) is a widely used chemical in the production of plastics but known to activate oestrogen receptors and linked by numerous studies to adverse effects on both human health and the environment. Here we demonstrate how SSbD can lead a multidisciplinary study for the identification of non-oestrogenic BPA analogues suitable for incorporation into high-performance polymeric materials. Toxicological evaluation of a library of 172 bisphenols using an in silico model identified 20 promising candidates that are synthesized from renewable lignin-sourced feedstocks via benign dehydrative catalytic routes. Subsequent in vitro assessment of their oestrogen receptor activity identifies bisguaiacol F as optimal BPA analogue, which is incorporated into a polyester with attractive thermal stability and flexibility. This work demonstrates an effective workflow for the discovery of renewable and non-oestrogenic bisphenols by taking advantage of the synergy of synthetic chemistry, toxicology and computational modelling.



