2025-11-19 ラトガース大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.rutgers.edu/news/engineers-develop-autonomous-artificial-intelligence-transforms-resilience-and-discovery
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10845-025-02638-w
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1526612525002671
製造プロセスの外挿モデリングのための大規模言語モデル Large language models for extrapolative modeling of manufacturing processes
Kiarash Naghavi Khanghah,AnandKumar Patel,Rajiv Malhotra & Hongyi Xu
Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing Published:24 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-025-02638-w
Abstract
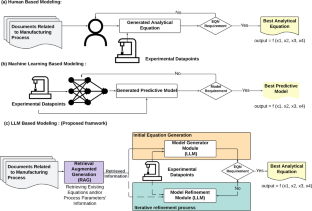
Conventional predictive modeling of parametric relationships in manufacturing processes is limited by the subjectivity of human expertise and intuition on the one hand and by the cost and time of experimental data generation on the other hand. This work addresses this issue by establishing a new Large Language Model (LLM) framework. The novelty lies in combining automatic extraction of process-relevant knowledge embedded in the literature with iterative model refinement based on a small amount of experimental data. This approach is evaluated on three distinct manufacturing processes that are based on machining, deformation, and additive principles. The results show that for the same small experimental data budget, the models derived by our framework have unexpectedly high extrapolative performance, often surpassing the capabilities of conventional Machine Learning. Further, our approach eliminates manual generation of initial models or expertise-dependent interpretation of the literature. The results also reveal the importance of the nature of the knowledge extracted from the literature and the significance of both the knowledge extraction and model refinement components.
現場積層造形における外部誘起欠陥のスケーラブルな制御 Scalable control of extraneously induced defects in in-field additive manufacturing
Jeremy Cleeman, Adrian Jackson, Shane Esola, Chenhui Shao, Hongyi Xu, Rajiv Malhotra
Journal of Manufacturing Processes Available online: 13 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2025.03.014
Highlights
- Addressed real-time defect mitigation under extraneous disturbances in in-field AM
- Created new Conditional Reinforcement Learning with implicit disturbance inclusion
- Enhanced speed of real-time defect mitigation by orders of magnitude
- Mitigation is generalizable without knowledge of disturbances or retraining.
- Broke knowledge-speed barrier in current solutions for such defect mitigation
Abstract
In-field Additive Manufacturing (AM) is exposed to irregular variations in process conditions (externalities) that affect defect dynamics. These externalities are invariable in conventional in-factory AM. Stoppage-free and real-time mitigation of part defects induced by these externality variations is necessary for timely delivery of quality parts in in-field AM. But existing solutions either require explicit knowledge of externality variations which is typically unavailable or they render the part unusable due to infeasibly slow defect mitigation. This work addresses this issue by establishing a novel Conditional Reinforcement Learning (ConRL) approach for rapid and real-time data-driven defect mitigation based on an implicit consideration of externality variations. Validation within a smart manufacturing pipeline on a Fused Filament Fabrication testbed reveals the unprecedented ability to mitigate defects at 10× greater speed via a single control action and within the same printed line. A hitherto unreported degree of scalability is observed, i.e., it is possible to mitigate defects induced by untrained-for, unknown and unmeasured externality variations without any retraining of the policy. The results also reveal new insight into the significance of conditionality in ConRL and of real-time defect quantification. The implications for wider adoption of ConRL to other in-field AM processes is discussed.