2025-10-30 愛媛大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.ehime-u.ac.jp/data_relese/pr_20251030_sci/
- https://www.ehime-u.ac.jp/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/pr_20251030_sci.pdf
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ae018f
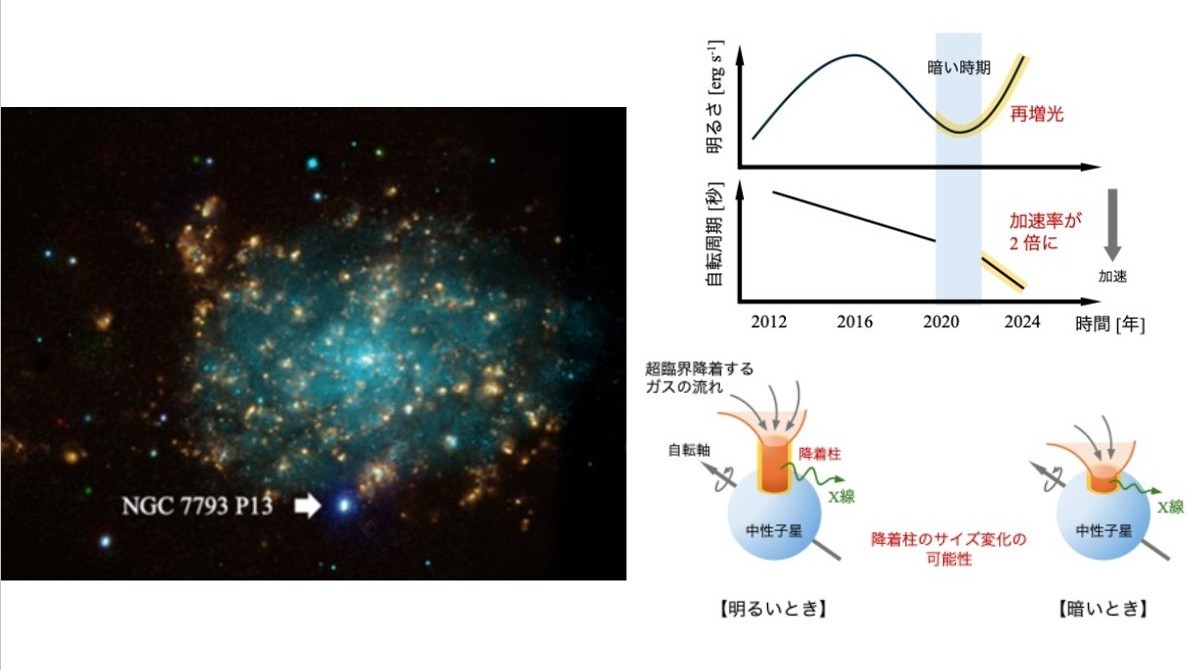
超高輝度X線パルサーNGC 7793 P13のスペクトルとタイミング特性のモニタリング Monitoring of the Spectral and Timing Properties of the Ultraluminous X-Ray Pulsar NGC 7793 P13
Marina Yoshimoto, Tomokage Yoneyama, Shogo B. Kobayashi, Hirokazu Odaka, Taiki Kawamuro, and Hironori Matsumoto
The Astrophysical Journal Letters Published: 2025 October 29
DOI:10.3847/2041-8213/ae018f
Abstract
We present the long-term spectral and timing evolution of the ultraluminous X-ray pulsar NGC 7793 P13 from 2011 to 2024 based on archival data from XMM-Newton, Chandra, NICER, and NuSTAR, including unpublished data after 2020. This data set enables us to investigate the observational properties across a long modulation of ∼10 yr. Although previous studies suggested an increasing trend in flux in 2020, we find that the pulsar decreased its flux to 2.6+0.7-0.7 ×10-14erg㎝-2s-1 in 2021, and rebrightened to 3.9+0.1-0.1 ×10-12erg㎝-2s-1 by 2024. Moreover, in the last two years, the spin-up rate was twice as large as that before 2020. However, the pulsed fraction was roughly as expected from an anticorrelation with the flux confirmed before 2020. Furthermore, we perform systematic phase-resolved spectroscopy to investigate the spectral evolution. The results show that, during the flux-decaying epoch, spectral hardness in the off-pulse phase softened while that in its on-pulse phase remained almost unchanged. This softening was not observable in the rebrightening epoch. Our results could provide new insights into the accretion geometry of neutron stars in supercritical accretion systems.



