2025-10-22 豊田工業大学
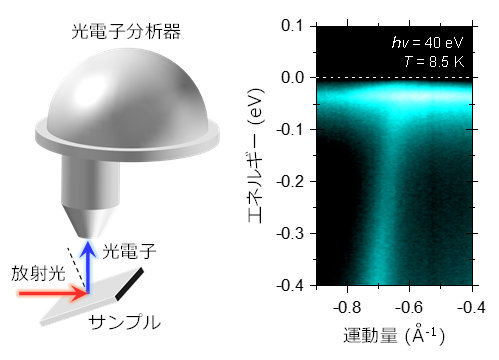
図1. 角度分解光電子分光の概念図(左)と今回の実験で得られたYbCu2Si2における電子のエネルギーと運動量の関係(右)。
<関連情報>
- https://www.toyota-ti.ac.jp/news/checktti/002829.html
- https://www.toyota-ti.ac.jp/news/files/20251022_ttipress_APL.pdf
- https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article-abstract/127/16/161903/3368606/Evidence-for-energy-dependent-scattering
重い電子系の熱電現象を支配するエネルギー依存散乱の証拠
Evidence for energy-dependent scattering dominating thermoelectricity in heavy fermion systems
Daiki Goto;Kentaro Kuga;Kiyohisa Tanaka;Tsunehiro Takeuchi;Masaharu Matsunami
Applied Physics Letters Published:October 20 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0291138
In the field of thermoelectric materials and devices, improving energy conversion efficiency remains a long-standing challenge. As a promising approach to address this issue, utilizing energy-dependent electron-scattering beyond the ordinary constant relaxation time approximation (CRTA) has been proposed. However, direct experimental evidence for an energy-dependent scattering reflected in the Seebeck coefficient is still lacking. Here, we demonstrate using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy that the relaxation time of heavy fermion quasiparticles is highly dependent on the energy near the Fermi level. The observed energy dependence of the relaxation time is due to the coherent Kondo scattering, describing the sign of the Seebeck coefficient reasonably well, which cannot be deduced from CRTA. Our findings provide not only deeper insight into the understanding of thermoelectricity in correlated materials but also future perspectives on possible orbital-selective engineering of thermoelectric materials.