2025-10-16 横浜市立大学
Web要約 の発言:
<関連情報>
- https://www.yokohama-cu.ac.jp/res-portal/news/20251016matsui.html
- https://www.yokohama-cu.ac.jp/res-portal/news/gjok7g00000029lz-att/20251016matsui1.pdf
- https://academic.oup.com/gigascience/article/doi/10.1093/gigascience/giaf115/8280287
比較ゲノミクスとマルチオミクス解析により、ヘベア属 におけるゴム生合成の進化と生理学的基盤が明らかになった Comparative genomics and multiomics analyses reveal the evolution and physiological basis of rubber biosynthesis in Hevea species
Nyok-Sean Lau, Emiko Okubo-Kurihara, Yuko Makita, Fetrina Oktavia, Tomoko Kuriyama, Yukio Kurihara, Hidefumi Hamasaki, Yuki Nakamura, Mitsutaka Kadota, Osamu Nishimura …
GigaScience Published:10 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giaf115
Abstract
Background
There are multiple species within the Hevea genus, each exhibiting distinct characteristics, but many remain underexplored due to their lower latex productivity. While Hevea brasiliensis is the primary source of natural rubber, other Hevea species represent valuable gene pools that could be leveraged in breeding programs to enhance latex yield, biosynthesis efficiency, and the physicochemical properties of latex. With increasing interest in enhancing natural rubber traits, these lesser-known species are being revisited for their underexplored genetic diversity.
Results
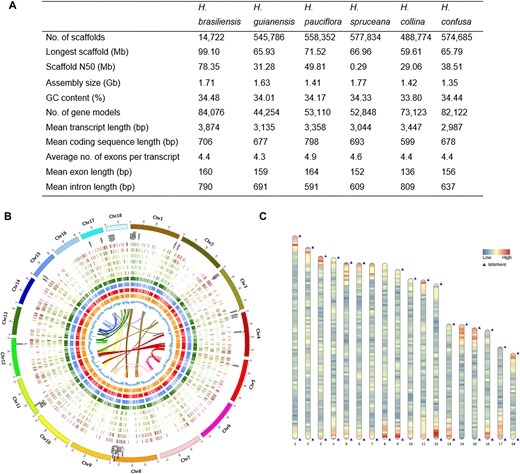
In this study, we performed a pangene analysis of 6 Hevea species and varieties, integrating proteomic and lipidomic data to investigate genetic and metabolic variation related to rubber biosynthesis and latex composition. The pangene analysis revealed conserved and expanded ATP-related functions, underscoring ATP’s role in latex production. The proteomic data identified key enzymes involved in rubber biosynthesis and differentially abundant proteins related to latex regeneration, suggesting that regeneration capacity may influence yield efficiency. Lipidomic profiling uncovered species-specific lipid compositions associated with membrane dynamics and rubber particle stability, which may contribute to latex properties.
Conclusions
These findings provide valuable insights into Hevea’s genomic and metabolic diversity, supporting future breeding programs aimed at improving natural rubber production and its performance in various applications.