2025-10-06 ウースター工科大学(WPI)
<関連情報>
- https://www.wpi.edu/news/announcements/using-ai-optimize-hydrogen-fuel-production-and-reduce-environmental-impact-wpi-research-published
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44286-025-00287-7
解釈可能な機械学習誘導型プラズマ触媒による水素製造 Interpretable machine learning-guided plasma catalysis for hydrogen production
Saleh Ahmat Ibrahim,Shengyan Meng,Charles Milhans,Magda H. Barecka,Yilang Liu,Qiang Li,Jiaqi Yang,Yabing Sha,Yanhui Yi & Fanglin Che
Nature Chemical Engineering Published:03 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44286-025-00287-7
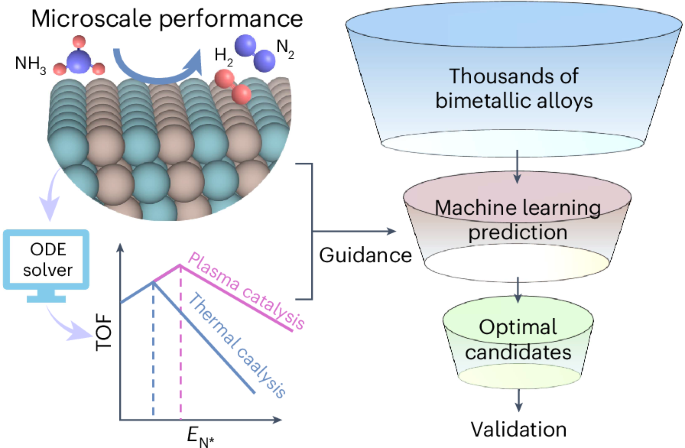
Abstract
Low-carbon ammonia decomposition via nonthermal plasma is a promising method for on-site hydrogen production, but finding optimal catalysts is challenging. Here we use multiscale simulations to link catalytic activity to nitrogen adsorption energy (EN) and identify the best catalysts for conventional heating and nonthermal plasma: Ru and Co, respectively. With an ideal EN of −0.51 eV for plasma catalysis, we applied machine learning to screen 3,300+ catalysts and designed efficient, earth-abundant alloys such as Fe3Cu, Ni3Mo, Ni7Cu and Fe15Ni. Plasma catalytic experiments at 400 °C further validated that the above alloys achieved higher conversions than the individual metals, and they also have comparable performance to Co. Our techno-economic analysis demonstrated potential economic benefits of plasma catalytic ammonia decomposition over Ni3Mo, highlighting a H2 production cost below the US$1 per kg H2 target and a low carbon footprint of ~0.91 kg of CO2 per kg H2.