2025-09-24 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=26150&pageIndex=1&searchCnd=&searchWrd=
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63784-6
人類世における前例のない世界的水不足の初出現 The first emergence of unprecedented global water scarcity in the Anthropocene
Vecchia P. Ravinandrasana & Christian L. E. Franzke
Nature Communications Published:23 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-63784-6
Abstract
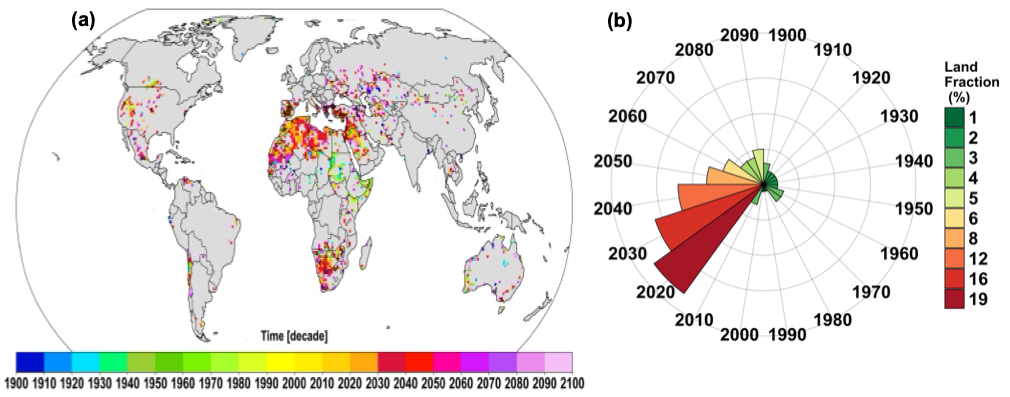
Access to water is crucial for all aspects of life. Anthropogenic global warming is projected to disrupt the hydrological cycle, leading to water scarcity. However, the timing and hotspot regions of unprecedented water scarcity are unknown. Here, we estimate the Time of First Emergence (ToFE) of drought-driven water scarcity events, referred to as “Day Zero Drought” (DZD), which arises from hydrological compound extremes, including prolonged rainfall deficits, reduced river flow, and increasing water consumption. Using a probabilistic framework and a large ensemble of climate simulations, we attribute the timing and likelihood of DZD events to human influence. Many regions, including major reservoirs, may face high risk of DZD by the 2020s and 2030s. Despite model and scenario uncertainties, consistent DZD hotspots emerge across the Mediterranean, southern Africa, and parts of North America. Urban populations are particularly vulnerable at the 1.5 °C warming level. The length of time between successive DZD events is shorter than the duration of DZD, limiting recovery periods and exacerbating water scarcity risks. Therefore, more proactive water strategies are urgently needed to avoid severe societal impacts of DZD.



