2025-09-12 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
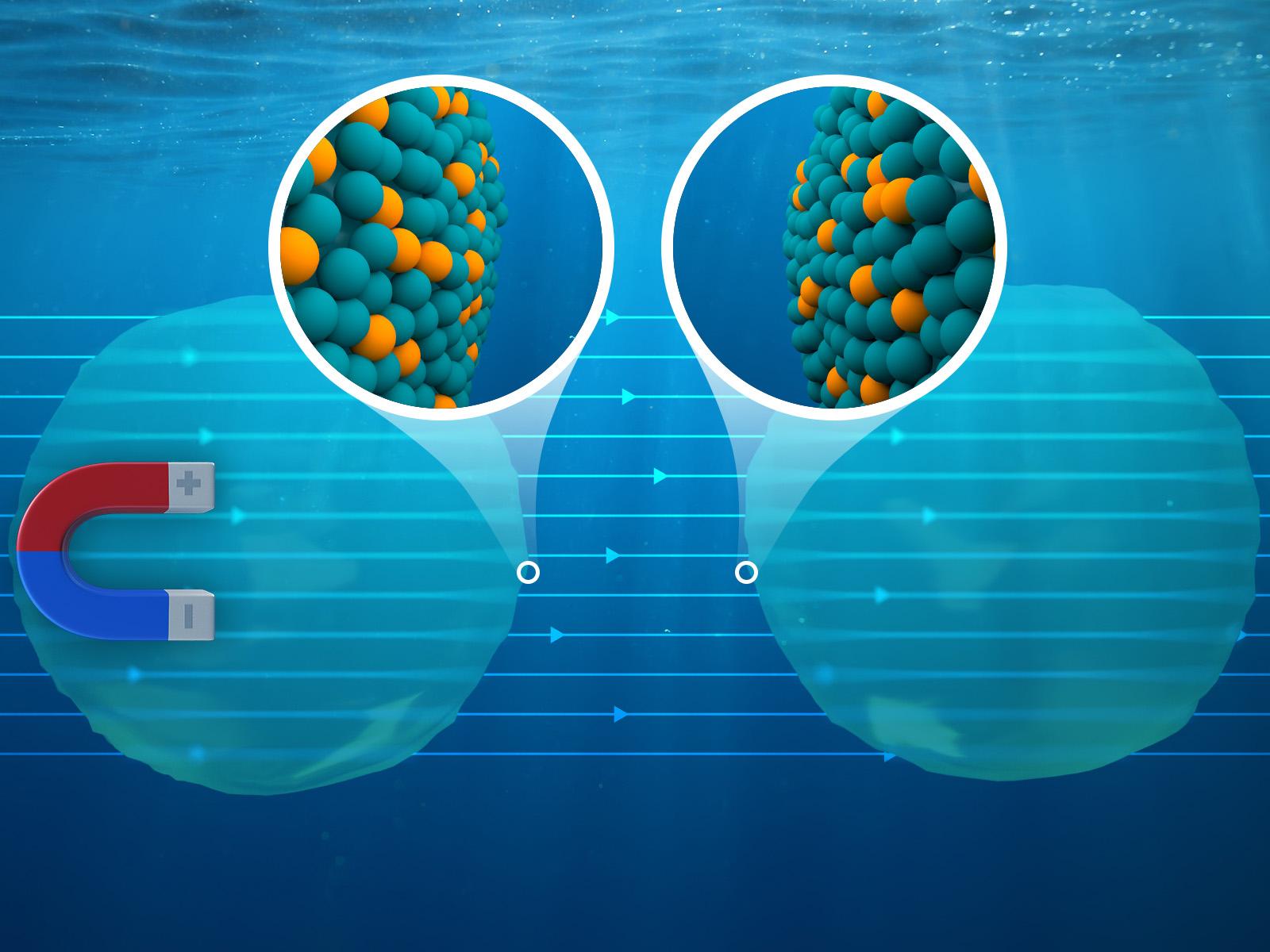
Modeling using surface magnetic regions to represent ion groups shows that magnetically driven interactions can compete with other intermolecular forces in solution.
(Image by Derek Munson | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory)
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/publications/nanoscale-interactions-magnetic-fields-critical-material-separations
- https://pubs.aip.org/aip/jcp/article/163/1/014502/3351077/Magnetic-interactions-between-nanoscale-domains-in
液体中におけるナノスケールドメイン間の磁気相互作用
Magnetic interactions between nanoscale domains in liquids
Mohammadhasan;Giovanna Ricchiuti;Andrew J. Ritchhart;Tao E. Li;Elias Nakouzi;Sebastian T. Mergelsberg;Venkateshkumar Prabhakaran;Jaehun Chun;Maria L. Sushko
The Journal of Chemical Physics Published:July 01 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0260005
Although external magnetic fields (eMFs) may influence effective interactions between nanoscale particles in liquids, their effects remain poorly understood. In this work, we introduce a simplified model of a solvated nanoparticle that consists of localized magnetic domains at its surface to represent groups of paramagnetic ions, forming nanodomains whose effective magnetic dipole moments are at least one order of magnitude greater than the individual ions. We use classical density functional theory to estimate the effective interactions between these localized magnetic nanoparticles (LMNPs) solvated in a diamagnetic solvent. Our findings indicate that, unlike individual ions, magnetic dipole interactions of nanodomains in the LMNP model can indeed compete with the electrostatic, van der Waals, and hydration interactions. Depending on the direction of eMF, the effective interactions between two LMNPs become more attractive or repulsive at relatively short separations on the order of 1 nm or less. This indicates that the interactions driven by an eMF play a critical role in aggregation for nanoparticles with magnetic nanodomains. The effective interactions between LMNPs show oscillatory behaviors that originate from the solvent correlations, which are not affected significantly in the presence of eMFs.



