2025-09-04バッファロー大学(UB)

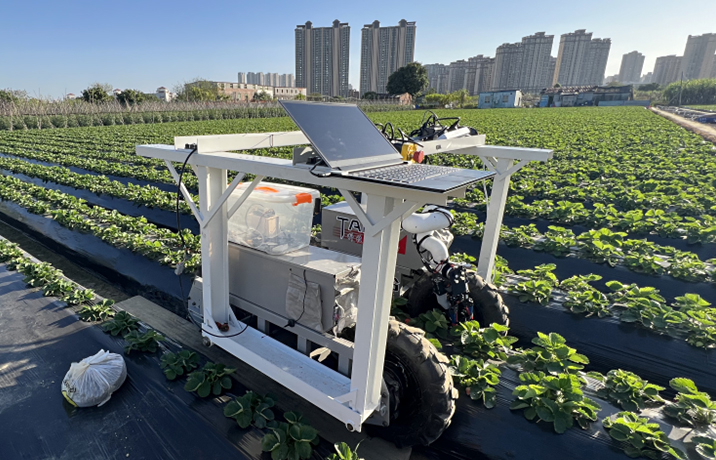
An illustration of a PFAS breakdown product in its negatively charged and neutral forms, depicted in a dynamic back-and-forth between these states. The accompanying chart illustrates a plot that allowed a University at Buffalo-led team to determine its acid dissociation constant or pKa. Credit: University at Buffalo
<関連情報>
- https://www.buffalo.edu/news/releases/2025/09/forever-chemicals-are-more-acidic-than-we-thought.html
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.estlett.5c00688
19 F-NMRによる10種類のPFAS、モノフルオロ酢酸、ジフルオロ酢酸、トリフルオロ酢酸のpKaの実験的測定 Experimental Determination of pKa for 10 PFAS, Mono-, Di-, and Trifluoroacetic Acid by 19F-NMR
Damalka Balasuryia,Aina Queral-Beltran,Tristan Vick,Scott Simpson,Silvia Lacorte,Diana S. Aga,and Alexander C. Hoepker
Environmental Science & Technology Letters Published: August 12, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5c00688
Abstract
Accurate pKa values of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are urgently needed to improve predictions of their environmental fate, bioaccumulation, and removal, yet reliable experimental data remain scarce. Here, we determined the pKa values of 10 PFAS and three short-chain fluorinated acids (MFA: 2.58 ± 0.03; DFA: 1.22 ± 0.03, TFA: 0.03 ± 0.08) using 19F and 1H NMR-based chemical shift perturbation. Results were compared to prior experimental values, OPERA predictions (CompTox), and our COSMO-RS calculations. Measured pKa values include PFPrA (−0.18 to −0.54), PFOA (−0.27 ± 0.18), PFBS and PFOS (< −1.85), 6:2 FTS (<0.0), GenX (−0.20 ± 0.09), NFDHA (−0.32 ± 0.18), PFMPA (−0.26 ± 0.13), and 6:2 FTUCA (2.59 ± 0.11). Across C2, C3, and C8 homologues, PFCAs exhibit pKa values of approximately −0.2 to −0.3. Telomerization markedly reduces acidity: 5:3 FTCA (pKa = 4.05 ± 0.04) is >104-fold less acidic than PFOA, with COSMO-RS predicting similar effects from PFOS to 6:2 FTS. The dominant acidifying influence arises from CF2 groups at C1 and C2 near COOH or SO3H. The unusually low pKa values for TFA, PFOA, and GenX reflect our low-MeOH, sorption-resistant NMR method. COSMO-RS consistently outperformed OPERA, underscoring the need for experimental benchmarks to improve predictive models for emerging PFAS.