2025-08-14 中国科学院(CAS)
Overview of the dynamic synchronicity paradigm for biomanufacturing (Image by Prof. WANG Weishan’s group)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202508/t20250818_1050912.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-025-02762-1
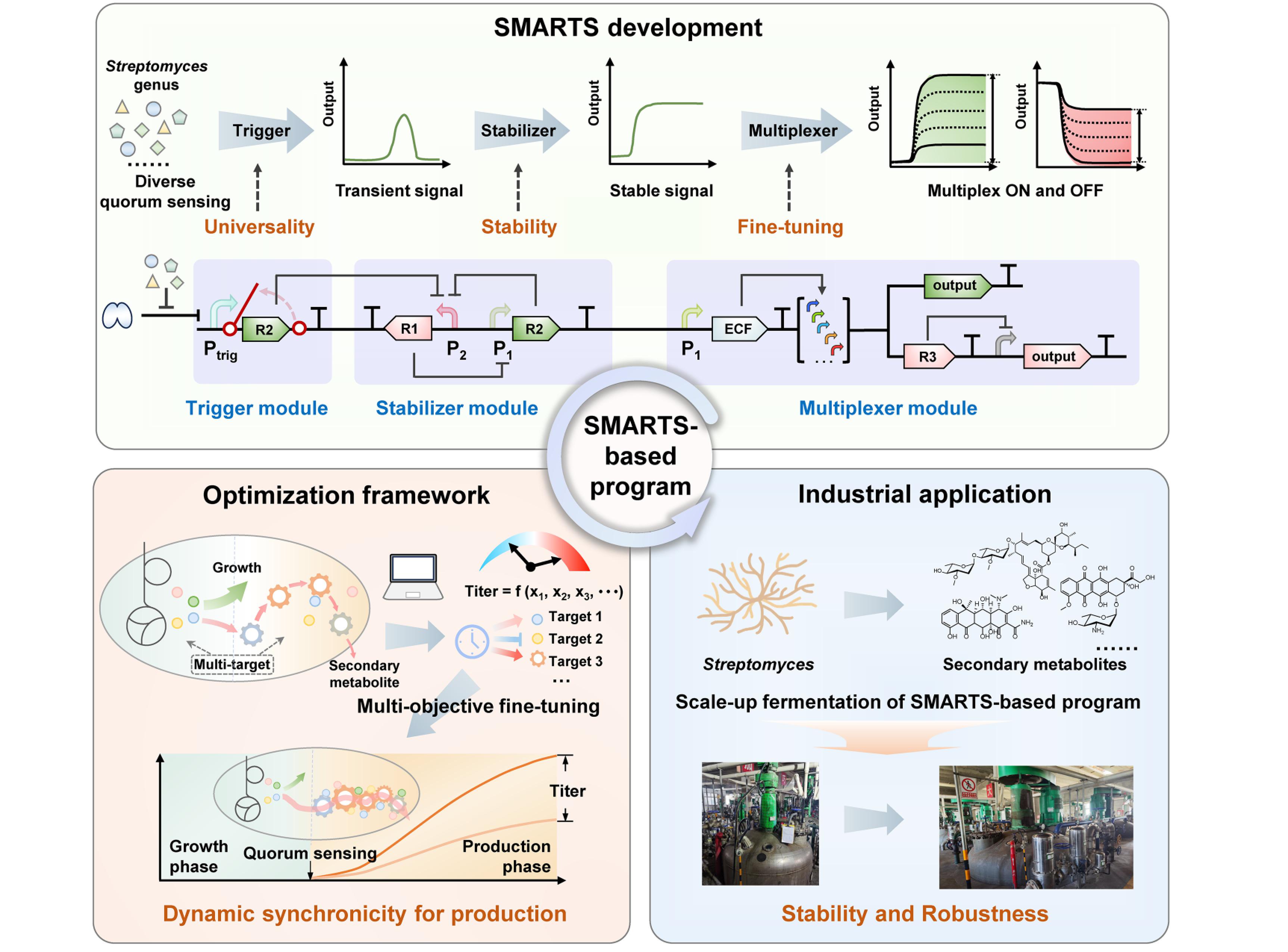
Streptomycesにおけるプラグアンドプレイシステムを用いた二次代謝産物のスケーラブルな生産 Scalable secondary metabolite production in Streptomyces using a plug-and-play system
Bowen Yang,Zilong Li,Jingyu Zhang,Shiwen Qiu,Xueting Liu,Zonglin Liang,Hao Yan,Yanyan Zhang,Lihong Liu,Bing Xia,Lianqun Bao,Defeng Li,Shanshan Zhou,Christophe Corre,Chengyu Zhang,Yinhua Lu,Gao-Yi Tan,Xuekui Xia,Shanshan Li,Lixin Zhang & Weishan Wang
Nature Biotechnology Published:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02762-1
Abstract
Streptomyces species are producers of bioactive secondary metabolites with clinical, agricultural and biotechnological applications. To scale these strains for industrial production, a plug-and-play system that orchestrates multitarget engineering for maximizing cellular contributions to secondary metabolites is needed. Building on the discovery that distinct quorum-sensing receptors within the Streptomyces genus can recognize an identical DNA-binding site, we build a quorum-sensing-triggered promoter applicable across various Streptomyces. Integrating this promoter with a stabilizer and a multiplexer module, we develop a Streptomyces multiplexed artificial control system (SMARTS) that converts the transient signals of diverse quorum sensing into stable and multiplexed on or off outputs with varying strengths. We build a redesigned native Streptomyces avermitilis for specialized production of the nematicide baiweimectin and a de novo programmed Streptomyces venezuelae for heterologous production of the semisynthesized antitumor drug epidoxorubicin. Notably, the baiweimectin-producing strain was scaled up to a 120-m3 industrial-scale fermentation with a titer of 8.4 g L−1, underscoring the robustness of the SMARTS-based program.



