2025-08-12 バッファロー大学 (UB)

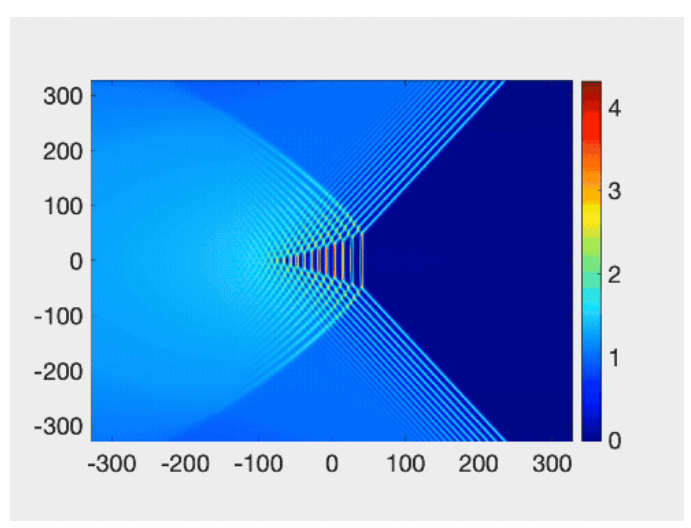
The research team’s simulation of two-dimensial wave patterns colliding, which looked similar to the “matrix tide” effect seen last year on the Qiantang River. Credit: Gino Biondini/University at Buffalo
<関連情報>
- https://www.buffalo.edu/news/releases/2025/08/math-describes-matrix-tides-and-other-complex-wave-patterns.html
- https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/cdvf-xnfw
2次元分散衝撃波の機械的反射と拡大 Mach Reflection and Expansion of Two-Dimensional Dispersive Shock Waves
Gino Biondini, Alexander Bivolcic, and Mark A. Hoefer
Physical Review Letters Published 5 August, 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/cdvf-xnfw
Abstract
The oblique collisions and dynamical interference patterns of two-dimensional dispersive shock waves are studied numerically and analytically via the temporal dynamics induced by wedge-shaped initial conditions for the Kadomtsev-Petviashvili II equation. Various asymptotic wave patterns are identified, classified, and characterized in terms of the incidence angle and the amplitude of the initial step, which can give rise to either subcritical or supercritical configurations, including the generalization to dispersive shock waves of the Mach reflection and expansion of viscous shocks and line solitons. An eightfold amplification of the amplitude of an obliquely incident flow upon a wall at the critical angle is demonstrated. Applications of the results include bore interactions in geophysical fluid dynamics.