2025-08-06 産業技術総合研究所
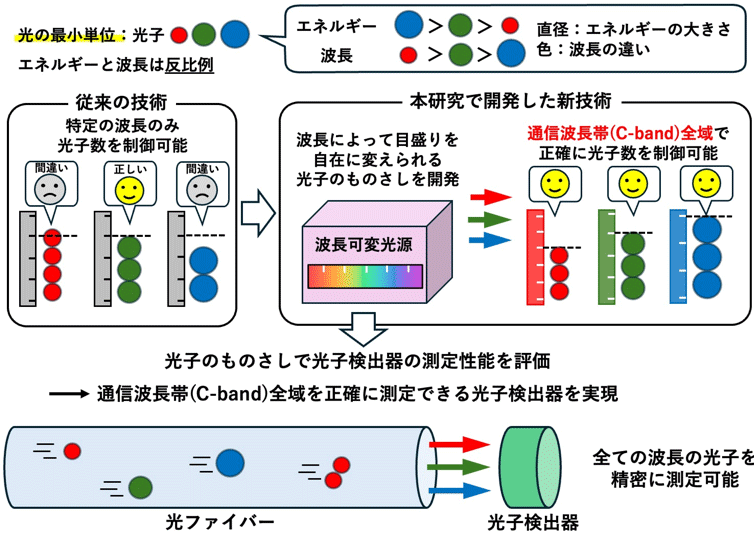
波長によって目盛りを自在に変えられる“光子のものさし”のイメージ
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20250806_3/pr20250806_3.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0030399225010059
Cバンド波長における移行エッジセンサーの検出効率の評価 Evaluation of detection efficiency of a transition edge sensor at C-band wavelength
Takeshi Jodoi, Tetsuya Tsuruta, Mauro Rajteri, Daiji Fukuda
Optics & Laser Technology Available online: 25 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2025.113414
Highlights
- We developed a calibration system for the C-band wavelength using laser pulses.
- Initial states were generated via laser by switching acoustic optical module.
- Input state photon statistics were evaluated by a second-order correlation function.
- Wavelength-dependent detection efficiency was precisely determined.
- Detection efficiency was evaluated by comparing experimental and simulation values.
Abstract
Photon-number-resolving detectors face strict demands regarding detection efficiency to meet the needs of quantum information processing. We constructed a system that can accurately evaluate system detection efficiency of a photon-number-resolving detector. We generated an optical pulse containing an arbitrary number of photons for the initial states by attenuated laser light; this pulse was used to evaluate the detection efficiency of the device under test. To generate this pulse, we modulated a continuous wavelength tunable laser using an acoustic optical modulator. From the photon statistics of the initial states, we found a second-order correlation function that was almost 1 at any wavelength, and these photon statistics followed a Poisson distribution. For the device under test, we evaluated the detection efficiency of a transition edge sensor and we employed two methods to calculate the number of detected photons. This value was calculated based on each photon state (method 1) or based on the zero photon state by assuming a Poisson distribution (method 2). Although the results of both methods were comparable within the range of uncertainty, method 2 yielded smaller uncertainty than method 1. We found that the wavelength-dependent detection efficiency was explained by the photon absorptance characteristics of the device under test. Additionally, the system detection efficiency varied from approximately 87 % to 93 %, and the expanded uncertainty values of methods 1 and 2 were 4.1 % and 1.5 %, respectively. This system enables the accurate evaluation of quantum states of photons at various wavelengths.