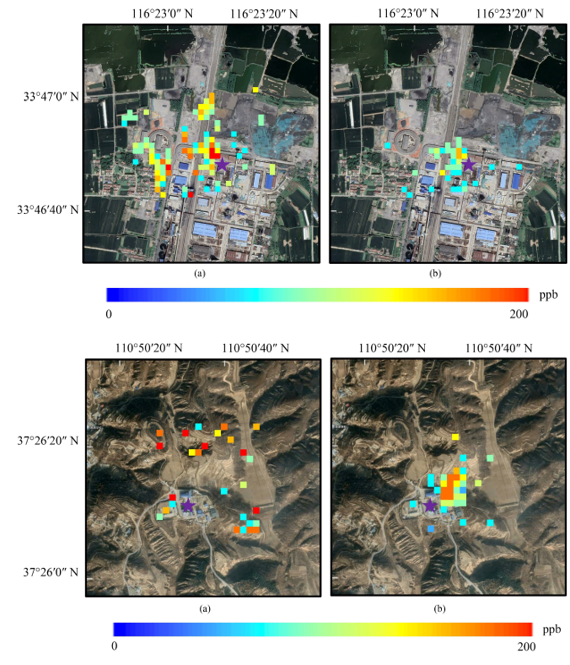
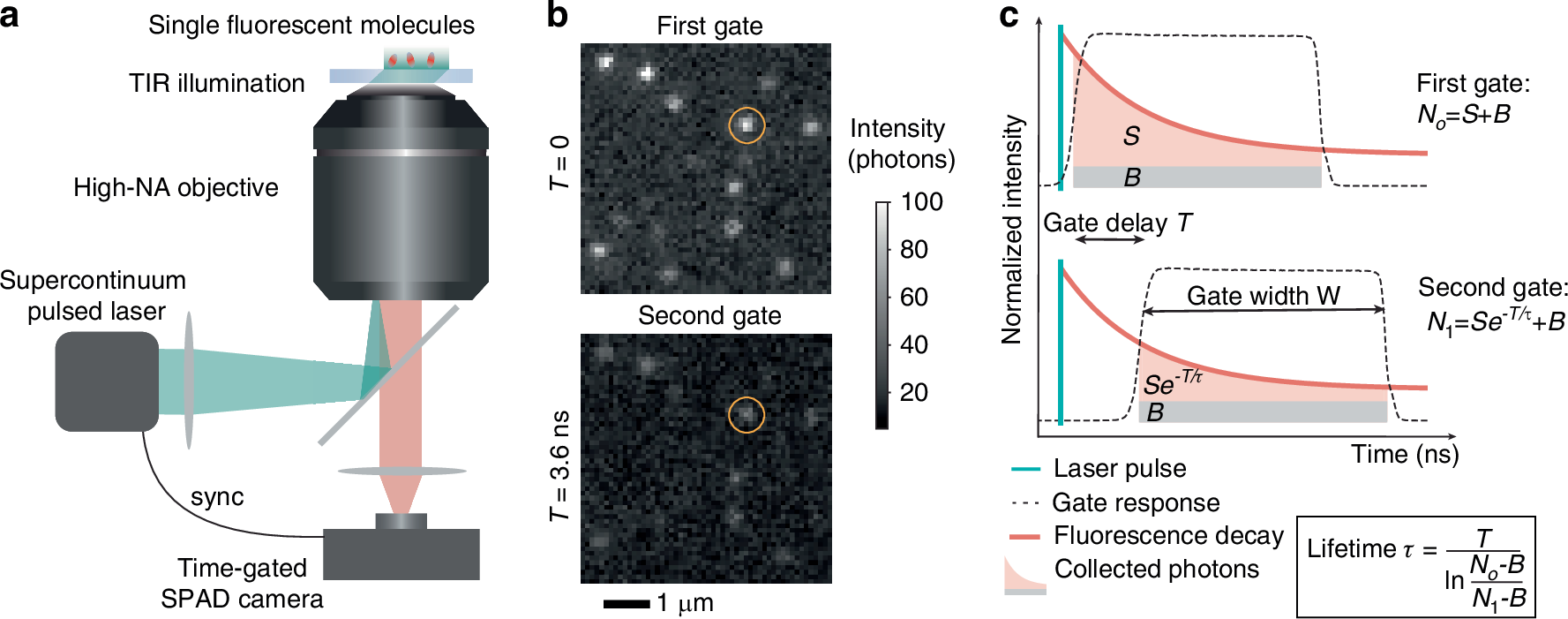
2025-08-05 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/cas_media/202508/t20250805_1049179.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-025-02305-8
二重成分の相乗効果を有するハイブリッド界面層により、21%の効率を実現した有機太陽電池 Organic solar cells with 21% efficiency enabled by a hybrid interfacial layer with dual-component synergy
Congqi Li,Yunhao Cai,Pengfei Hu,Tao Liu,Lei Zhu,Rui Zeng,Fei Han,Ming Zhang,Meng Zhang,Jikai Lv,Yuanxin Ma,Dexia Han,Meng Zhang,Qijie Lin,Jingwen Xu,Na Yu,Jiawei Qiao,Jiarui Wang,Xin Zhang,Jianlong Xia,Zheng Tang,Long Ye,Xiaoyi Li,Zihao Xu,… Hui Huang
Nature Materials Published:18 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02305-8
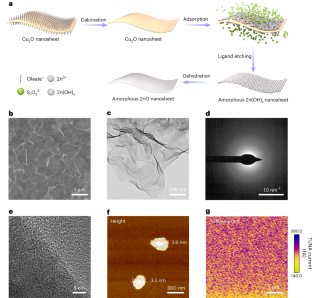
Abstract
The cathode interfacial layer (CIL) critically influences electron extraction and charge recombination, thereby playing a pivotal role in organic solar cells (OSCs). However, most state-of-the-art CILs are constrained by limited conductivity, high recombination and poor morphology, which collectively hinder device efficiency and stability. Here we report an inorganic–organic hybrid CIL (AZnO-F3N), developed by a dual-component synergy strategy, which integrates organic material PNDIT-F3N with two-dimensional amorphous zinc oxide. This design leverages the synergistic interactions between two-dimensional amorphous zinc oxide and PNDIT-F3N, resulting in reduced interfacial defect, enhanced conductivity and improved film uniformity. OSCs incorporating the AZnO-F3N CIL exhibit more efficient charge extraction and transport, along with reduced recombination. Consequently, a D18:L8-BO-based binary OSC achieves an efficiency of 20.6%. The introduction of BTP-eC9 as the third component further elevates the efficiency to 21.0% (certified as 20.8%). Moreover, the CIL demonstrates versatility across various active layers, thick-film configuration and flexible devices, underscoring its great potential to advance OSC technology.