2025-06-30 中国科学院(CAS)
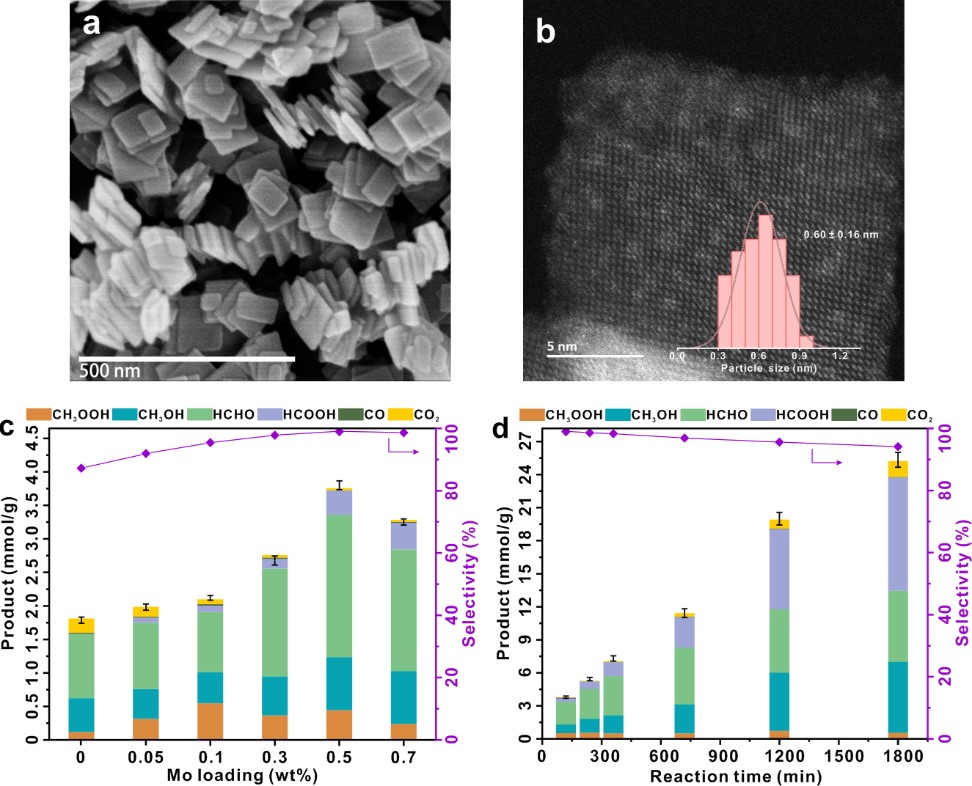 a. SEM image of TiO2; b, ACHAADF-STEM image of 0.5MoOx-TiO2; c. Photocatalytic activity and selectivity for methane oxidation over catalysts with different Mo loadings; d. Photocatalytic activity and selectivity for methane oxidation over the 0.5MoOx-TiO2 catalyst with extended reaction time. (Image by APM)
a. SEM image of TiO2; b, ACHAADF-STEM image of 0.5MoOx-TiO2; c. Photocatalytic activity and selectivity for methane oxidation over catalysts with different Mo loadings; d. Photocatalytic activity and selectivity for methane oxidation over the 0.5MoOx-TiO2 catalyst with extended reaction time. (Image by APM)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/chem/202507/t20250701_1046527.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-59465-z
TiO2を用いた光触媒によるCH4の酸素酸塩への変換反応におけるサブナノMoOxクラスターによる過酸化の抑制 Subnanometric MoOx clusters limit overoxidation during photocatalytic CH4 conversion to oxygenates over TiO2
Panpan Wu,Yueying Chu,Maoling Wang,Ningdong Feng,Jun Xu,Ding Ma,Jinhua Ye & Feng Deng
Nature Communications Published:06 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59465-z
Abstract
Direct photocatalytic oxidation of methane to high-value-added oxygenated products remains a great challenge due to the unavoidable overoxidation of target products. Here, we report an efficient and highly selective TiO2 photocatalyst anchored with subnanometric MoOx clusters for photocatalytic methane oxidation to organic oxygenates by oxygen. A high organic oxygenates yield of 3.8 mmol/g with nearly 100% selectivity was achieved after 2 h of light irradiation, resulting in a 13.3% apparent quantum yield at 365 nm. Mechanistic studies reveal a photocatalytic cycle for methane oxidation on the MoOx anchored TiO2, which not only largely inhibits the formation of hydroxyl and superoxide radicals and the overoxidation of oxygenate products but also facilitates the activation of the first carbon-hydrogen bond of methane. This work would promote the rational design of efficient non-noble metal catalysts for direct conversion of methane to high-value-added oxygenates.