2025-06-24 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/chem/202506/t20250623_1045951.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44286-025-00238-2
選択的かつ高速なイオン輸送のための界面高分子架橋による超薄膜の作製 Ultrathin membranes prepared through interfacial polymer cross-linking for selective and fast ion transport
Xiaonan Liu,Mengqi Shi,Chenyi Liao,Na Ta,Yiwen Chen,Congzhi Deng,Hongjun Zhang,Wenjing Lu & Xianfeng Li
Nature Chemical Engineering Published:20 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44286-025-00238-2
Abstract
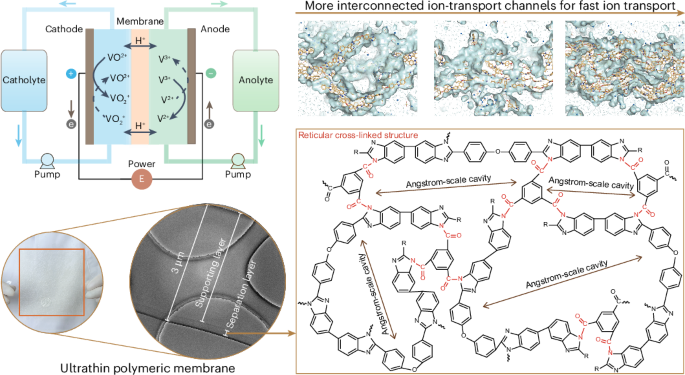
Ion-selective membranes are widely used in water treatment and batteries. However, it is challenging to obtain membranes that are both selective and permeable. Here, we report an interfacial polymer cross-linking strategy to produce ultrathin but robust polymeric membranes that are simultaneously permeable and selective. Cross-linking the polymer at the interface of two immiscible solvents followed by nonsolvent exchange produces a 3-µm-thick ultrathin membrane that contains a nanoscale separation layer with a quasi-ordered reticular cross-linking structure. Besides conferring strength, the cross-linked structures have angstrom-scale channels and ion-selective sites that can precisely separate ions of similar sizes and charges. We show that these membranes enable increased working current density and power density of various aqueous flow batteries. This strategy resolves a long-standing challenge in polymeric membranes.