2025-06-09 中国科学院(CAS)
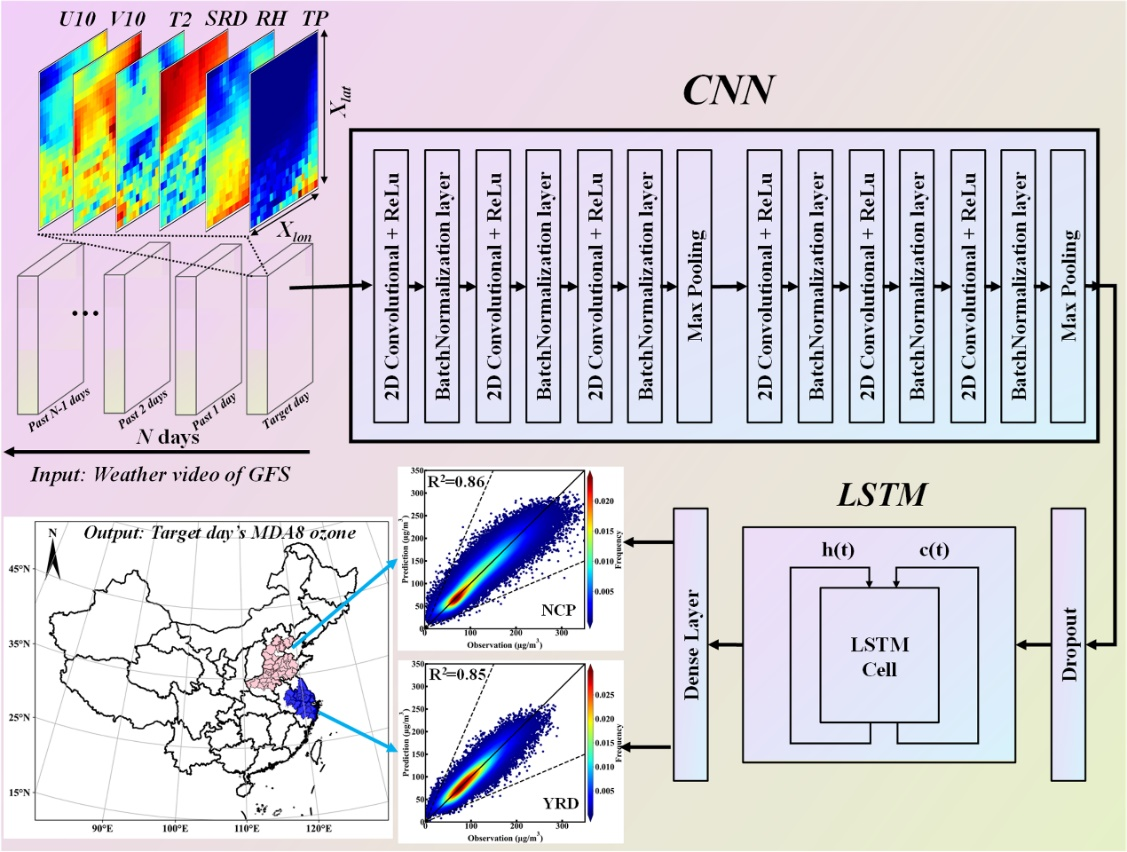 気象プロセスの時空間的進化特性を統合したCNN-LSTM機械学習フレームワーク(画像提供:HU Feng)
気象プロセスの時空間的進化特性を統合したCNN-LSTM機械学習フレームワーク(画像提供:HU Feng)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/tech/202506/t20250610_1045333.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.4c11988
中国華北平原と長江デルタにおけるオゾン変動と地域気象過程のマッピング Mapping Regional Meteorological Processes to Ozone Variability in the North China Plain and the Yangtze River Delta, China
Feng Hu,Pinhua Xie,Jin Xu,Xin Tian,Zhidong Zhang,Yansheng Lv,Qiang Zhang,Youtao Li,and Wen-qing Liu
Environmental Science & Technology Published: May 8, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.4c11988
Abstract
High-concentration ozone threatens human health and ecosystems, modulated by dynamic, multiscale meteorological processes. Existing machine learning studies for ozone prediction rarely incorporate the spatiotemporal evolution of regional meteorological fields (STRMFs), limiting the explanatory power of meteorological drivers in ozone variability. Thus, a sequential convolutional long short-term memory network framework (CNN-LSTM) was designed to utilize the STRMFs for ozone prediction. Scenarios incorporating STRMFs across multiple spatiotemporal scales were constructed using Global Forecast System (GFS) data sets. Model performance was evaluated in terms of ozone concentration prediction accuracy (AOCP) and precision in forecasting high-ozone pollution events (PHOE) across key Chinese regions. Appropriate expansion of meteorological data spatiotemporal scale enhanced AOCP, with notable improvements in PHOE, demonstrating ozone variability’s dependence on multiscale meteorological processes. Leveraging meteorological data that better represent real atmospheric conditions improved AOCP. The CNN-LSTM framework explained over 85% of daily ozone variability through STRMF integration, successfully resolving how ozone concentration variations in key regions responded to typhoon positional shifts. This methodology enables timely pollution alerts while elucidating the critical role of regional meteorological processes in ozone pollution.



