2025-06-05 統計数理研究所
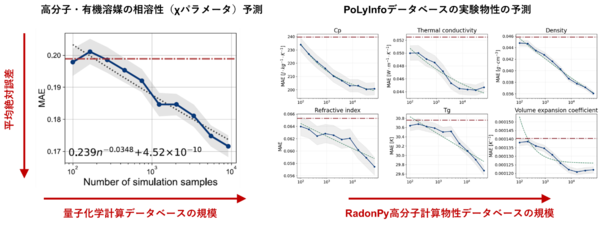
図 1: Sim2Real転移学習スケーリング則を観測することに成功
<関連情報>
- https://www.ism.ac.jp/ura/press/ISM2025-03.html
- https://www.ism.ac.jp/ura/press/ISM2025-03/pr.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41524-025-01606-5
実世界予測のための計算材料データベースの拡張におけるSim2Real転移学習のスケーリング則 Scaling Law of Sim2Real transfer learning in expanding computational materials databases for real-world predictions
Shunya Minami,Yoshihiro Hayashi,Stephen Wu,Kenji Fukumizu,Hiroki Sugisawa,Masashi Ishii,Isao Kuwajima,Kazuya Shiratori & Ryo Yoshida
npj Computational Materials Published:24 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-025-01606-5
Abstract
To address the challenge of limited experimental materials data, extensive physical property databases are being developed based on high-throughput computational experiments, such as molecular dynamics simulations. Previous studies have shown that fine-tuning a predictor pretrained on a computational database to a real system can result in models with outstanding generalization capabilities compared to learning from scratch. This study demonstrates the scaling law of simulation-to-real (Sim2Real) transfer learning for several machine learning tasks in materials science. Case studies of three prediction tasks for polymers and inorganic materials reveal that the prediction error on real systems decreases according to a power-law as the size of the computational data increases. Observing the scaling behavior offers various insights for database development, such as determining the sample size necessary to achieve a desired performance, identifying equivalent sample sizes for physical and computational experiments, and guiding the design of data production protocols for downstream real-world tasks.



