2025-06-02 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
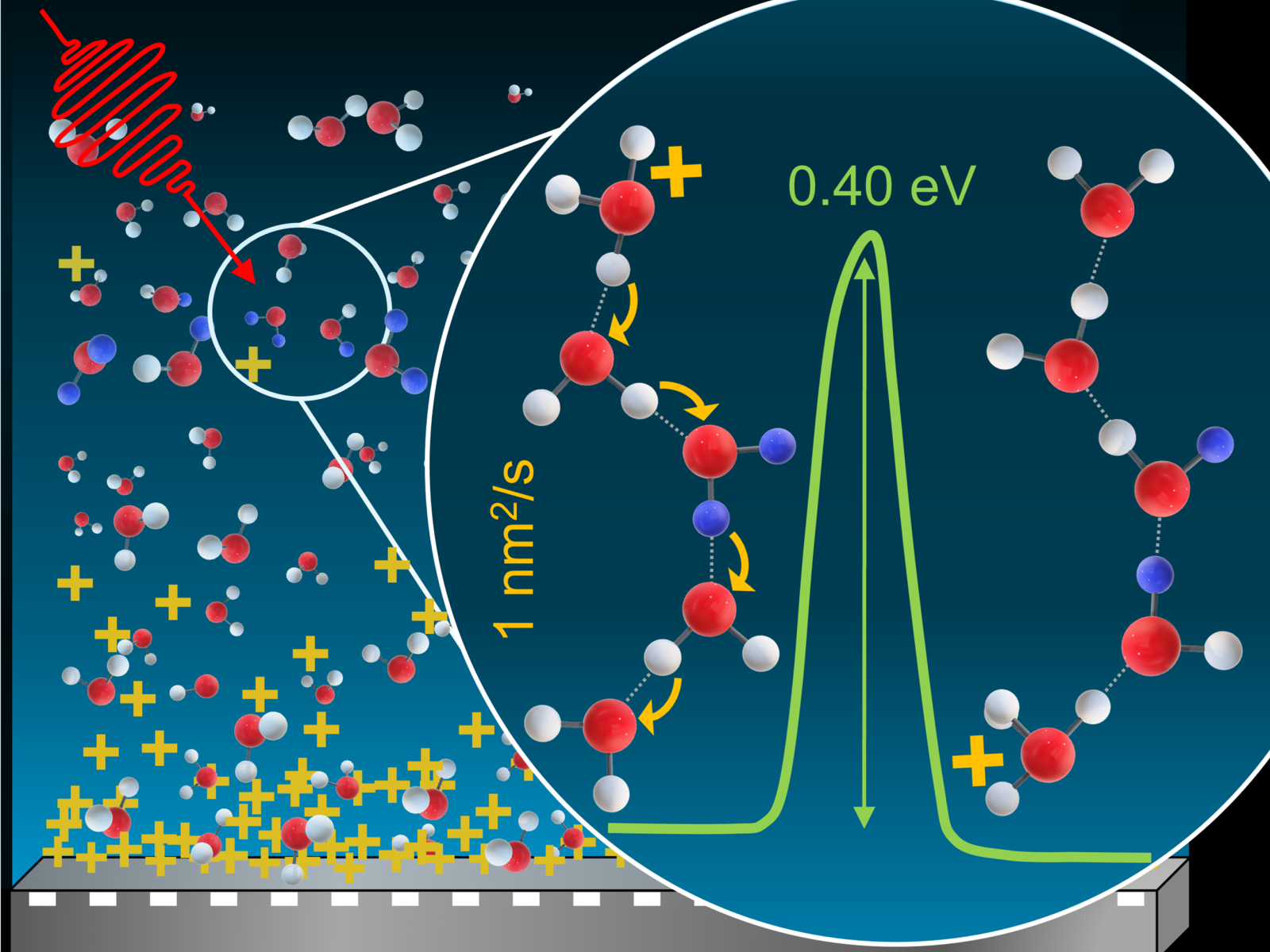 Hydrogen–deuterium exchange data provide information about the spatial distribution of protons within amorphous solid water, the energy barrier required for proton diffusion, and the proton diffusion coefficient.
Hydrogen–deuterium exchange data provide information about the spatial distribution of protons within amorphous solid water, the energy barrier required for proton diffusion, and the proton diffusion coefficient.
(Image by Megan Dunlap | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory)
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/publications/measuring-proton-diffusion-supercooled-water
- https://pubs.aip.org/aip/jcp/article/161/24/244504/3328439/Proton-diffusion-and-hydrogen-deuterium-exchange
114~134Kのアモルファス固体水におけるプロトン拡散と水素・重水素交換
Proton diffusion and hydrogen/deuterium exchange in amorphous solid water at temperatures from 114 to 134 K
Megan K. Dunlap;Loni Kringle;Bruce D. Kay;Greg A. Kimmel
The Journal of Chemical Physics: December 26 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0233755
The reaction coefficient for hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) exchange and the diffusion of hydrated excess protons within amorphous solid water (ASW) are characterized as a function of temperature. For these experiments, water films are deposited on a Pt(111) substrate at 108 K, and reactions with pre-adsorbed hydrogen atoms produce hydrated protons. Upon heating, protons diffuse within the water, and H/D exchange occurs when they encounter D2O probe molecules deposited in the films. The time-dependent concentration of D2O is monitored with infrared spectroscopy, and it indicates the protons diffusion from the substrate and establish an equilibrium distribution prior to significant H/D exchange for temperatures 114 K≤T≤ 134 K. By controlling the distance between the D2O molecules and the substrate, we probe the distribution of protons within the film. It decays as x−2 for the examined range of x (12–52 nm) due to the electric field that develops between the diffusing protons and their image charges in the metal substrate. This agrees with the theoretical distance scaling for the equilibrated proton concentration in a dielectric near a metal boundary. From the proton concentration and the measured D2O decay rate, a lower bound for the proton diffusion coefficient ranging from 10−20 m2/s at 114 K to 10−18 m2/s at 134 K is estimated. The diffusion coefficient has an activation energy of 0.40 eV, which is comparable to energies reported for molecular translations and rotations of H2O, suggesting they may play a critical role in the proton diffusion mechanism within ASW.