2025-05-28 ジョージア大学(UGA)

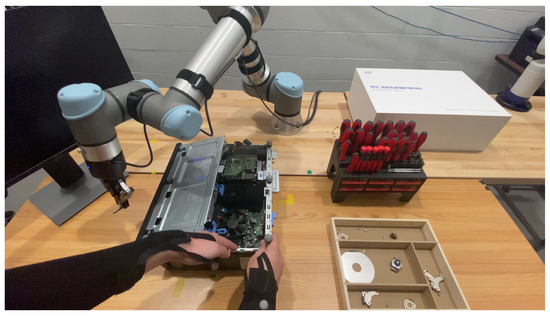
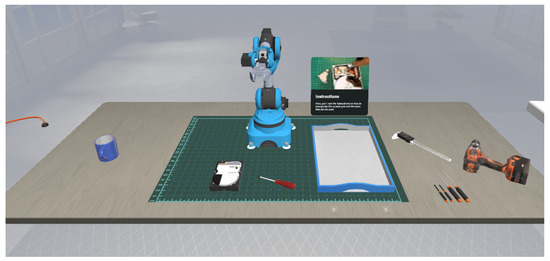
The VR Co-Lab program places users in a digital environment similar to what they may see in the workplace, where they can learn to work with robots. (Submitted)
<関連情報>
- https://news.uga.edu/vr-could-help-train-employees-working-with-robots/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1702/13/3/239
VR Co-Lab: 人間とロボットの分解トレーニングと合成データ生成のためのバーチャルリアリティプラットフォーム VR Co-Lab: A Virtual Reality Platform for Human–Robot Disassembly Training and Synthetic Data Generation
Yashwanth Maddipatla,Sibo Tian,Xiao Liang,Minghui Zheng and Beiwen Li
Machines Published: 17 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13030239
Abstract
This research introduces a virtual reality (VR) training system for improving human–robot collaboration (HRC) in industrial disassembly tasks, particularly for e-waste recycling. Conventional training approaches frequently fail to provide sufficient adaptability, immediate feedback, or scalable solutions for complex industrial workflows. The implementation leverages Quest Pro’s body-tracking capabilities to enable ergonomic, immersive interactions with planned eye-tracking integration for improved interactivity and accuracy. The Niryo One robot aids users in hands-on disassembly while generating synthetic data to refine robot motion planning models. A Robot Operating System (ROS) bridge enables the seamless simulation and control of various robotic platforms using Unified Robotics Description Format (URDF) files, bridging virtual and physical training environments. A Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model predicts user interactions and robotic motions, optimizing trajectory planning and minimizing errors. Monte Carlo dropout-based uncertainty estimation enhances prediction reliability, ensuring adaptability to dynamic user behavior. Initial technical validation demonstrates the platform’s potential, with preliminary testing showing promising results in task execution efficiency and human–robot motion alignment, though comprehensive user studies remain for future work. Limitations include the lack of multi-user scenarios, potential tracking inaccuracies, and the need for further real-world validation. This system establishes a sandbox training framework for HRC in disassembly, leveraging VR and AI-driven feedback to improve skill acquisition, task efficiency, and training scalability across industrial applications.