2025-05-22 中国科学院 (CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202505/t20250521_1044189.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08965-5
矮小銀河における予期せぬクラスター形成パターンが銀河形成モデルに挑む Unexpected clustering pattern in dwarf galaxies challenges formation models
Ziwen Zhang,Yangyao Chen,Yu Rong,Huiyuan Wang,Houjun Mo,Xiong Luo & Hao Li
Nature Published:21 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08965-5
Abstract
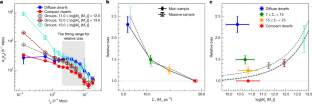
The galaxy correlation function serves as a fundamental tool for studying cosmology, galaxy formation and the nature of dark matter. It is well established that more massive, redder and more compact galaxies tend to have stronger clustering in space1,2. These results can be understood in terms of galaxy formation in cold dark matter (CDM) halos of different mass and assembly history. Here we report an unexpectedly strong large-scale clustering for isolated, diffuse and blue dwarf galaxies, comparable to that seen for massive galaxy groups but much stronger than that expected from their halo mass. Our analysis indicates that the strong clustering aligns with the halo assembly bias seen in simulations3 with the standard ΛCDM cosmology only if more diffuse dwarfs formed in low-mass halos of older ages. This pattern is not reproduced by existing models of galaxy evolution in a ΛCDM framework4,5,6, and our finding provides clues for the search of more viable models. Our results can be explained well by assuming self-interacting dark matter7, suggesting that such a scenario should be considered seriously.