2025-05-18 清華大学
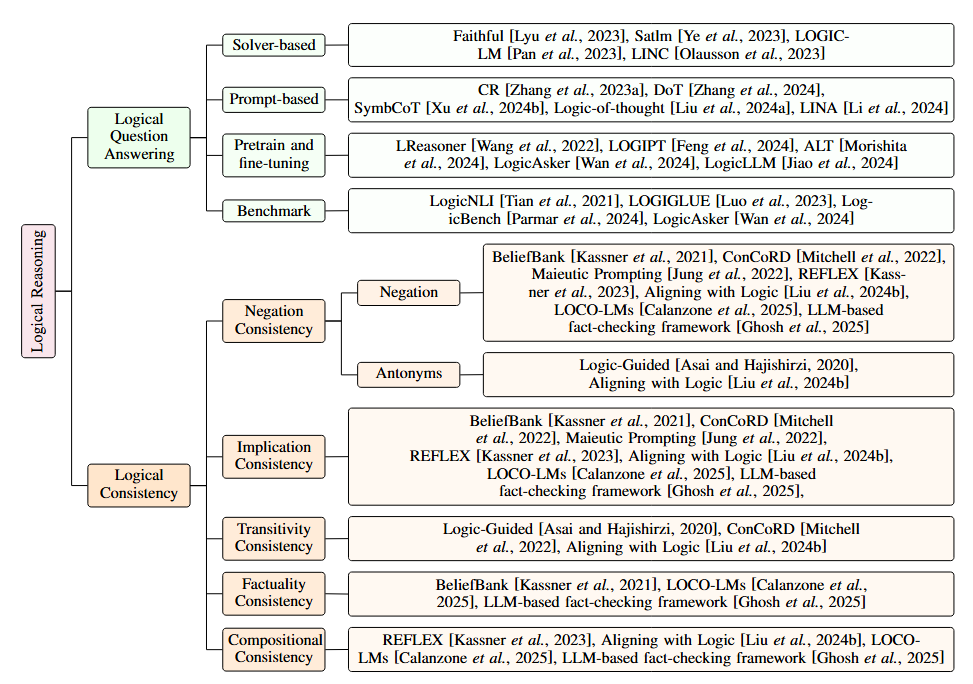 Research Survey Classification Framework as proposed in the paper
Research Survey Classification Framework as proposed in the paper
<関連情報>
LLMを論理的推論で強化する: 包括的な調査 Empowering LLMs with Logical Reasoning: A Comprehensive Survey
Fengxiang Cheng, Haoxuan Li, Fenrong Liu, Robert van Rooij, Kun Zhang, Zhouchen Lin
arXiv last revised 24 Feb 2025 (this version, v2)
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2502.15652
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable successes on various natural language tasks. However, recent studies have found that there are still significant challenges to the logical reasoning abilities of LLMs. This paper summarizes and categorizes the main challenges into two aspects: (1) Logical question answering, LLMs often fail to generate the correct answer within complex logical problem which requires sophisticated deductive, inductive or abductive reasoning given a collection of premises and constrains. (2) Logical consistency, LLMs are prone to producing responses contradicting themselves across different questions. For example, a state-of-the-art Macaw question-answering LLM answers Yes to both questions Is a magpie a bird? and Does a bird have wings? but answers No to Does a magpie have wings?. To facilitate this research direction, we comprehensively investigate the most cutting-edge methods and propose detailed taxonomies of these methods. Specifically, to accurately answer complex logic questions, previous methods can be categorized based on reliance on external solvers, prompts, pretraining, and fine-tuning. To avoid logical contradictions, we discuss concepts and solutions of various logical consistencies, including implication, negation, transitivity, factuality consistency, and their composites. In addition, we review commonly used benchmark datasets and evaluation metrics, and discuss promising research directions, such as extensions to modal logic to account for uncertainty, and efficient algorithms satisfying multiple logical consistencies simultaneously.