2025-04-24 中国科学院(CAS)
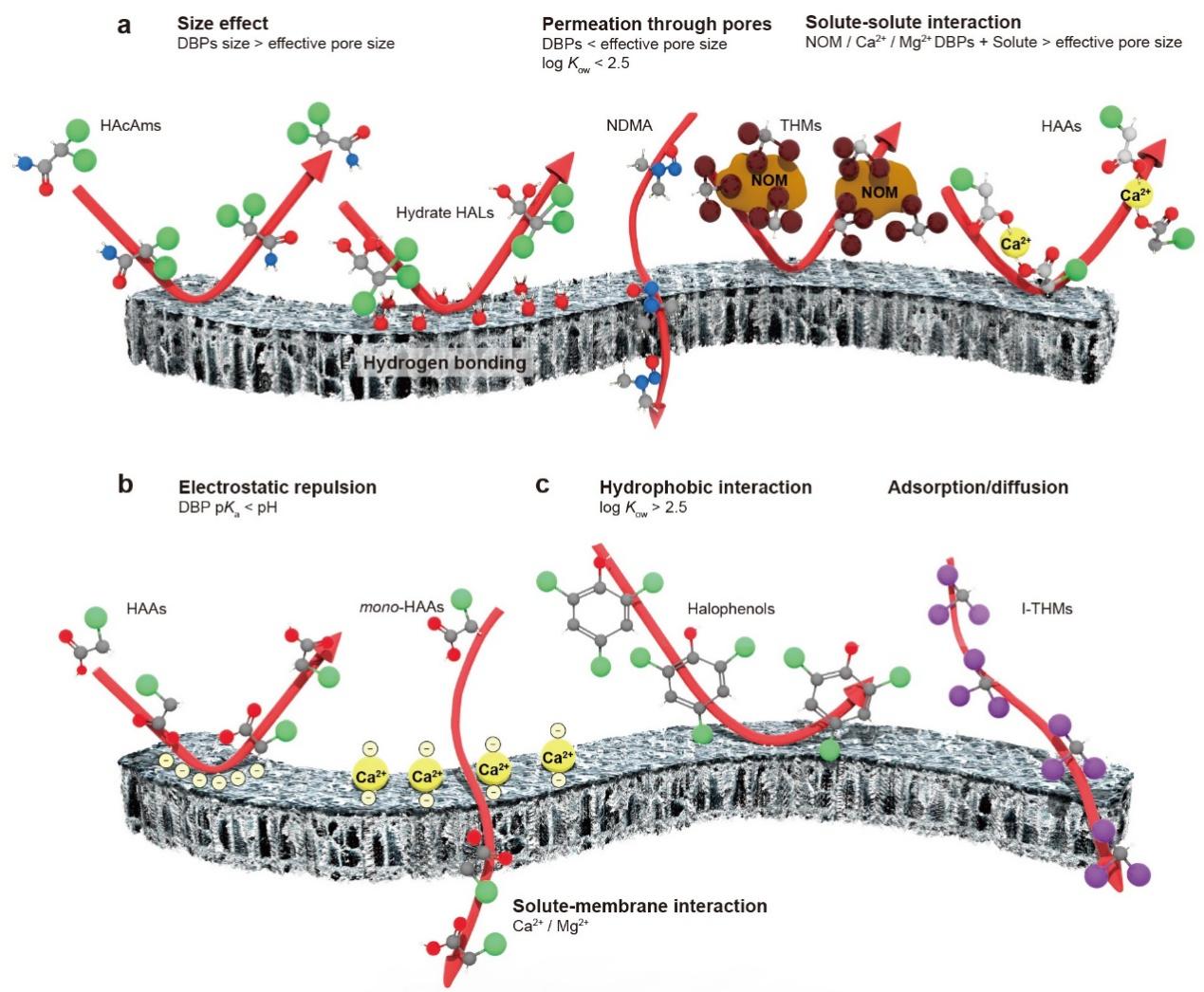 Image by Dr. WANG Lei
Image by Dr. WANG Lei
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202504/t20250424_1041940.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44221-025-00413-y
消毒副産物除去のためのナノろ過および逆浸透技術 Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis technologies for disinfection by-product removal
Lei Wang,Chuyang Y. Tang,Yunxia Hu,Baiyang Chen & Wei Xing
Nature Water Published:16 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-025-00413-y
Abstract
The presence of disinfection by-products (DBPs) in drinking water poses substantial health risks, necessitating effective removal strategies. Although nanofiltration and reverse osmosis (RO) show promise in DBP removal, their full potential remains largely unexplored. Here we examine DBP rejection by nanofiltration/RO, focusing on membrane characteristics, DBP properties, water quality and operating conditions. Optimization strategies, such as reducing the effective pore size, increasing surface charge and roughness, and improving desalination capacity, can enhance size-exclusion, electrostatic repulsion and overall DBP rejection efficiency. Feed water quality and operational conditions affect removal efficiency by altering membrane pore structure, surface charge and DBP speciation. Membrane ageing can impair neutral-DBP removal and enhance charged-DBP removal. Notably, small, hydrophilic and neutral DBP species pose challenges for effective rejection and warrant prioritized mitigation efforts. Overall, a comprehensive understanding of the interactions among membranes, DBPs, water components and operating conditions is crucial for effectively minimizing DBP risk.