2025-04-15 東京大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/news/release/20250415.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-025-02870-4
結晶成長に対する不純物の影響 Impact of impurities on crystal growth
Qiong Gao,Huang Fang,Dong Xiang,Yanshuang Chen,Hajime Tanaka & Peng Tan
Nature Physics Published:15 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02870-4
Abstract
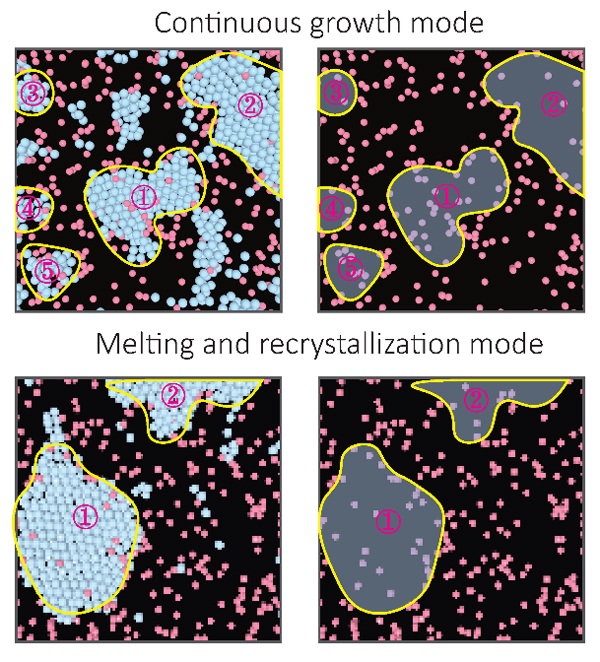
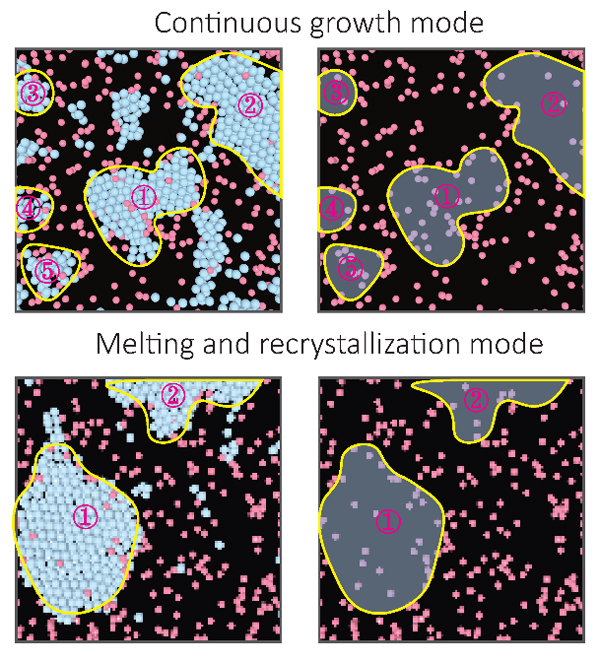
Impurities critically influence crystallization, a process fundamental to both physical sciences and industrial engineering. However, understanding how impurity transport affects crystallization presents substantial experimental challenges. Here we visualized crystallization at the single-particle level for a relatively high concentration of impurities. We observed a bifurcation in growth modes—continuous growth or melting and recrystallization—governed by the ability of the system to remove impurity particles from the growth front. The initial nucleation configuration determines the crystal grain size and growth-front morphology, which in turn influence impurity transport. Small grains promote lateral impurity transport to grain boundaries, thus reducing impurity concentration and favouring continuous growth, whereas larger grains accumulate impurities, leading to melting and recrystallization. We reveal that the latter arises from the competition between crystallization and vitrification, which is a form of devitrification. This study provides insights into the relation between impurity concentration and crystallization pathways and highlights how the initial configuration shapes the final crystal morphology.