2025-03-21 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2025/device-enables-direct-communication-among-multiple-quantum-processors-0321
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-025-02811-1
キラル量子インターコネクトを用いた決定論的遠隔エンタングルメント Deterministic remote entanglement using a chiral quantum interconnect
Aziza Almanakly,Beatriz Yankelevich,Max Hays,Bharath Kannan,Réouven Assouly,Alex Greene,Michael Gingras,Bethany M. Niedzielski,Hannah Stickler,Mollie E. Schwartz,Kyle Serniak,Joel Î-j. Wang,Terry P. Orlando,Simon Gustavsson,Jeffrey A. Grover &William D. Oliver
Nature Physics Published:21 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02811-1
Abstract
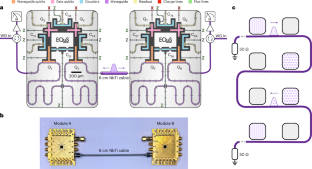
Quantum interconnects facilitate entanglement distribution between non-local computational nodes in a quantum network. For superconducting processors, microwave photons are a natural means to mediate this distribution. However, many existing architectures limit node connectivity and directionality. In this work, we construct a chiral quantum interconnect between two nominally identical modules in separate microwave packages. Our approach uses quantum interference to emit and absorb microwave photons on demand and in a chosen direction between these modules. We optimize our protocol using model-free reinforcement learning to maximize the absorption efficiency. By halting the emission process halfway through its duration, we generate remote entanglement between modules in the form of a four-qubit W state with approximately 62% fidelity in each direction, limited mainly by propagation loss. This quantum network architecture enables all-to-all connectivity between non-local processors for modular and extensible quantum simulation and computation.