2025-02-27 ロイヤルメルボルン工科大学(RMIT)
<関連情報>
- https://www.rmit.edu.au/news/all-news/2025/feb/sea-sponge-lattice
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0263822324009632
深海スポンジに着想を得た格子構造のオーセティック挙動とエネルギー吸収特性 Auxetic behavior and energy absorption characteristics of a lattice structure inspired by deep-sea sponge
Jiaming Ma、Hongru Zhang、Ting-Uei Lee、Hongjia Lu、Yi Min Xie、Ngoc San Ha
複合構造 オンライン公開日: 2024 年 12 月 27 日
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2024.118835

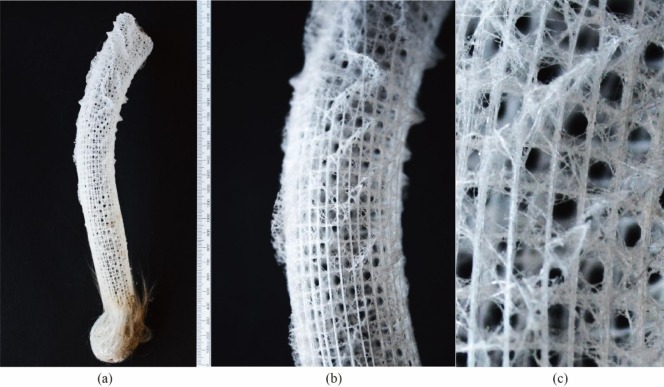
Fig. 1. The skeletal system of the Euplectella aspergillum, showing: (a) the entire skeletal tube, (b) a magnified view highlighting its regular lattice-like structure, and (c) the detailed pattern of alternating open and closed cells.
Abstract
Auxetic metamaterials, characterized by their lateral contraction under compression, have seen notable progress in recent years, largely due to advancements in 3D printing technologies. However, their practical application remains constrained by limited design versatility, moderate improvements in negative Poisson’s ratio (NPR), and relatively low structural stiffness. To address these challenges, a bio-inspired lattice structure (BLS) has been developed, drawing inspiration from the skeletal system of deep-sea hexactinellid sponges, renowned for their exceptional energy absorption capabilities, stiffness, and mechanical properties. Although this structure exhibits auxetic behavior, a comprehensive understanding of its mechanical performance, including its auxetic properties, remains incomplete. In this study, we systematically explore the auxetic behavior, stiffness, and energy absorption properties of the BLS through a combination of quasi-static compression experiments and detailed numerical simulations using finite element analysis. The experimental results reveal that the BLS outperforms conventional auxetic structures, such as re-entrant hexagonal honeycombs, in terms of NPR, stiffness, and energy absorption capacity. Furthermore, a parametric study is conducted to evaluate the influence of geometric variations, such as member thickness and spacing, on the mechanical performance of the BLS. These findings demonstrate that the BLS has the potential to pioneer a new class of auxetic materials, offering superior mechanical properties and broad applicability in engineering fields that require enhanced energy absorption and structural stiffness under compressive loading.