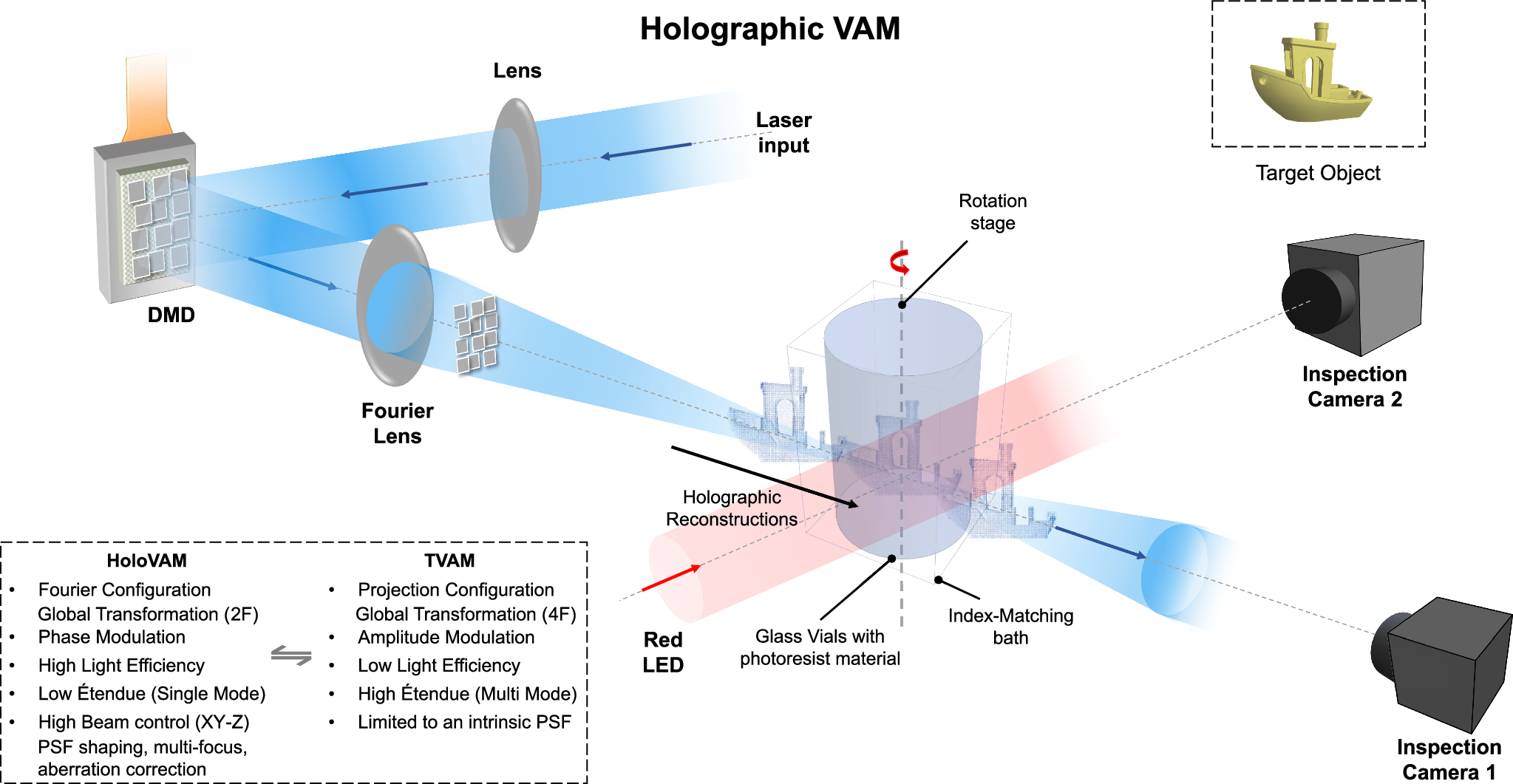
2025-02-17 スウェーデン王立工科大学 (KTH)
<関連情報>
- https://www.kth.se/en/om/nyheter/centrala-nyheter/ai-on-aircraft-can-reduce-risk-of-mid-air-stalls-and-sudden-drops-1.1385785
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-56408-6
乱流分離バブルにおける能動的流動制御のための深層強化学習 Deep reinforcement learning for active flow control in a turbulent separation bubble
Bernat Font,Francisco Alcántara-Ávila,Jean Rabault,Ricardo Vinuesa & Oriol Lehmkuhl
Nature Communications Published:07 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56408-6
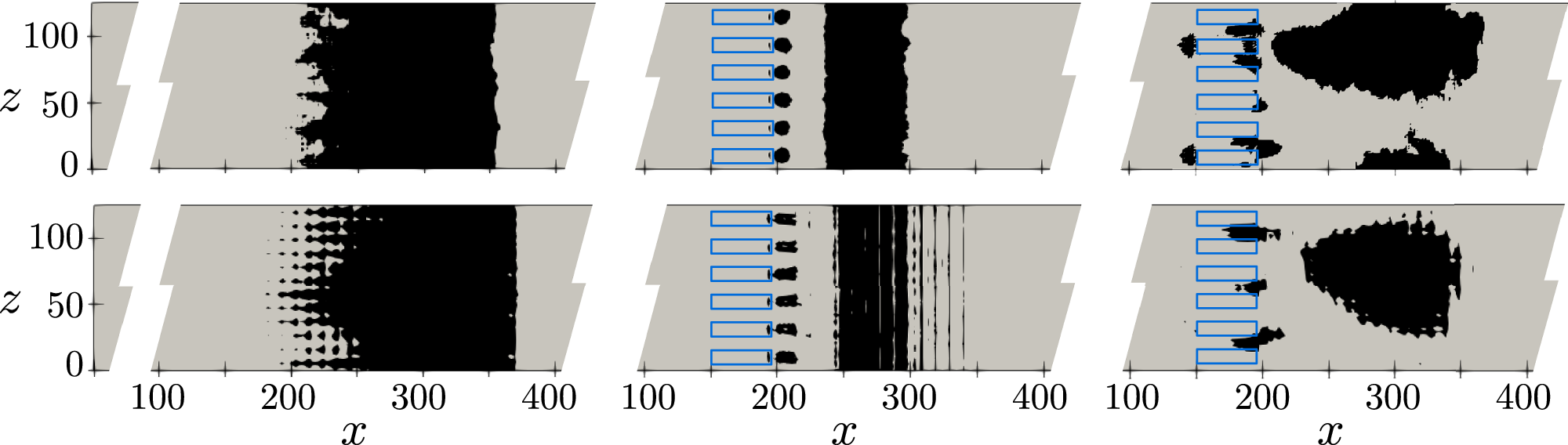
Abstract
The control efficacy of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) compared with classical periodic forcing is numerically assessed for a turbulent separation bubble (TSB). We show that a control strategy learned on a coarse grid works on a fine grid as long as the coarse grid captures main flow features. This allows to significantly reduce the computational cost of DRL training in a turbulent-flow environment. On the fine grid, the periodic control is able to reduce the TSB area by 6.8%, while the DRL-based control achieves 9.0% reduction. Furthermore, the DRL agent provides a smoother control strategy while conserving momentum instantaneously. The physical analysis of the DRL control strategy reveals the production of large-scale counter-rotating vortices by adjacent actuator pairs. It is shown that the DRL agent acts on a wide range of frequencies to sustain these vortices in time. Last, we also introduce our computational fluid dynamics and DRL open-source framework suited for the next generation of exascale computing machines.