2024-11-07 アメリカ合衆国・イリノイ大学アーバナ・シャンペーン校
<関連情報>
- https://news.illinois.edu/view/6367/1396654060?utm_medium=web&utm_campaign=yksphyseng&utm_source=nb
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-52630-w
酸化還元電気透析と電気吸着の統合による超短鎖~長鎖PFASの除去 Integrating redox-electrodialysis and electrosorption for the removal of ultra-short- to long-chain PFAS
Nayeong Kim,Johannes Elbert,Ekaterina Shchukina & Xiao Su
Nature Communications Published:27 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-52630-w
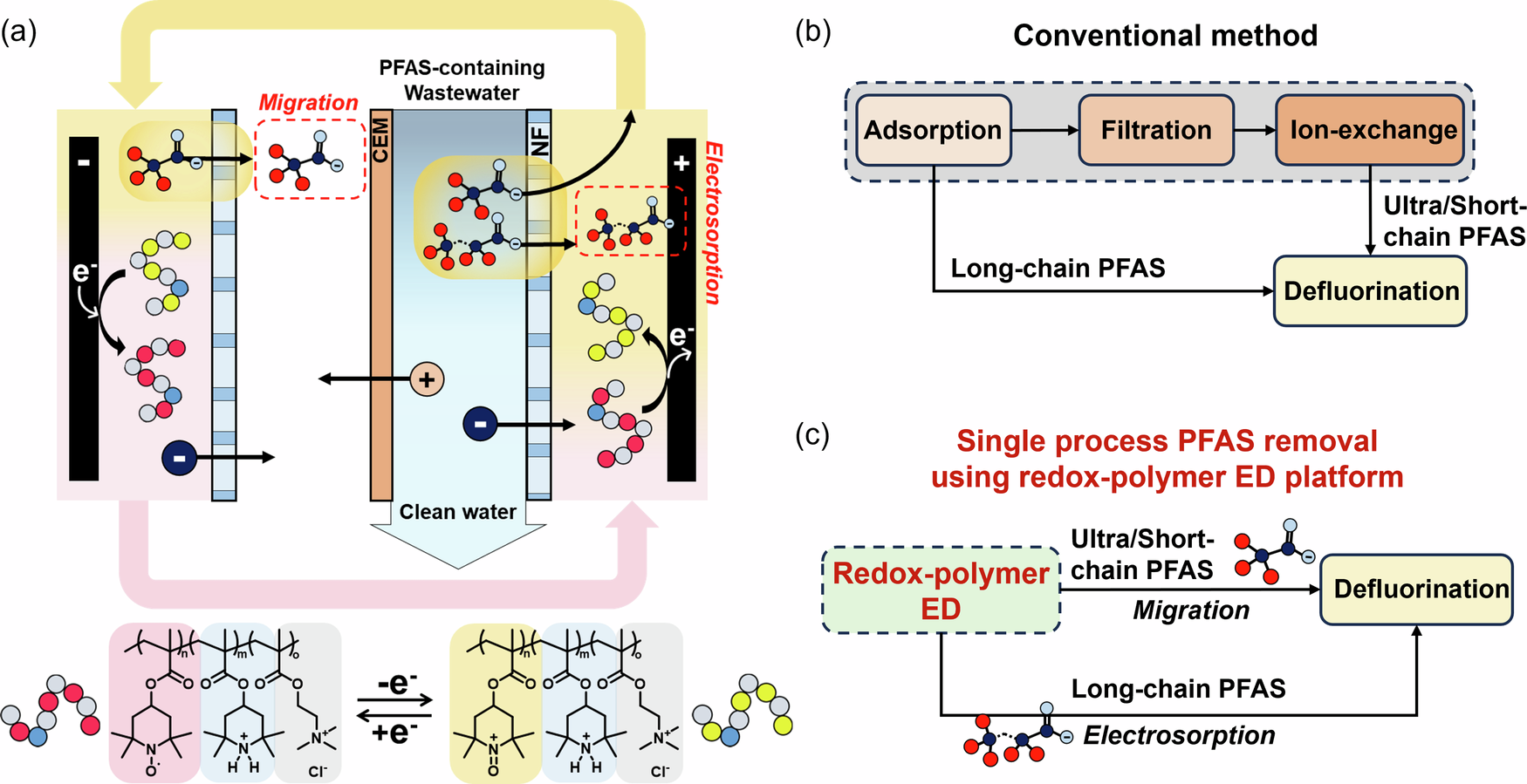
Abstract
A major challenge in per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) remediation has been their structural and chemical diversity, ranging from ultra-short to long-chain compounds, which amplifies the operational complexity of water treatment and purification. Here, we present an electrochemical strategy to remove PFAS from ultra-short to long-chain PFAS within a single process. A redox-polymer electrodialysis (redox-polymer ED) system leverages a water-soluble redox polymer with inexpensive nanofiltration membranes, facilitating the treatment of varied chain lengths of PFAS without membrane fouling. Our approach combines both ion migration by electrodialysis (for PFAS with chain lengths ≤C4) and electrosorption strategies (for PFAS with chain lengths ≥C6) to eliminate approximately 90% of ultra-short-, short-chain, and long-chain PFAS. At the same time, we achieve continuous desalination of the source water down to potable water level. The redox-polymer ED exhibits remarkable PFAS removal in real source water scenarios, including from matrices with 10,000 times higher salt concentrations, as well as secondary effluents from wastewaters. Additionally, the removed PFAS is mineralized with a defluorination performance between 76-100% by electrochemical oxidation, highlighting the viability of integrating the separation step with a reactive degradation process.



