2023-09-28 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
◆再充電可能バッテリー内の固体電極と液体電解質の境界での電気特性を直接測定する初めての研究結果がNature Energyに掲載されました。この研究を率いたのは、米国エネルギー省太平洋西北国立研究所の研究チームで、従来の考えと異なり、いわゆる固体電解質間層(SEI)は電子の絶縁体ではなく、半導体のように振る舞うことを示しています。これにより、液体電解質の物理的および電気化学的特性を微調整することで、より持続可能なバッテリーの設計に直接的な影響を与える可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/news-media/new-twist-rechargeable-battery-performance
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-023-01361-1
リチウム金属アノード上の固体電解質間相の電気特性をその場で直接測定 Direct in situ measurements of electrical properties of solid–electrolyte interphase on lithium metal anodes
Yaobin Xu,Hao Jia,Peiyuan Gao,Diego E. Galvez-Aranda,Saul Perez Beltran,Xia Cao,Phung M. L. Le,Jianfang Liu,Mark H. Engelhard,Shuang Li,Gang Ren,Jorge M. Seminario,Perla B. Balbuena,Ji-Guang Zhang,Wu Xu & Chongmin Wang
Nature Energy Published:28 September 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01361-1
Abstract
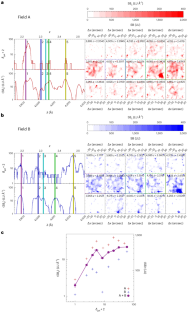
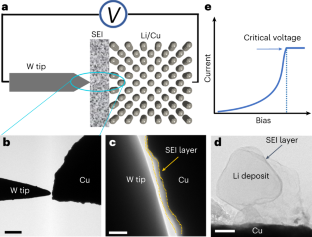
The solid–electrolyte interphase (SEI) critically governs the performance of rechargeable batteries. An ideal SEI is expected to be electrically insulative to prevent persistently parasitic reactions between the electrode and the electrolyte and ionically conductive to facilitate Faradaic reactions of the electrode. However, the true nature of the electrical properties of the SEI remains hitherto unclear due to the lack of a direct characterization method. Here we use in situ bias transmission electron microscopy to directly measure the electrical properties of SEIs formed on copper and lithium substrates. We reveal that SEIs show a voltage-dependent differential conductance. A higher rate of differential conductance induces a thicker SEI with an intricate topographic feature, leading to an inferior Coulombic efficiency and cycling stability in Li||Cu and Li||LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 cells. Our work provides insight into the targeted design of the SEI with desired characteristics towards better battery performance.