2023-08-17 カリフォルニア大学バークレー校(UCB)
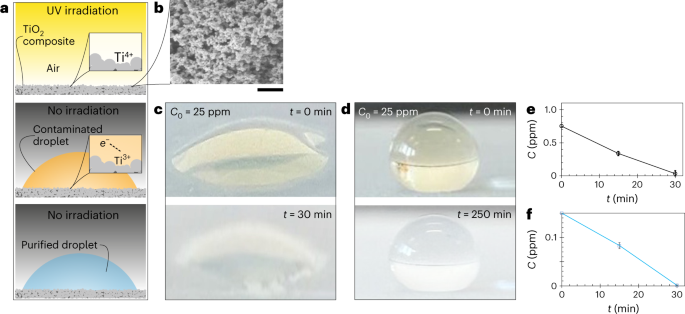
◆太陽光を利用する特殊なコーティングを持つナノエンジニアリングされた鋼メッシュを使用し、収集した霧水を浄化して飲料水にする手法を実証。このハイブリッドアプローチは、収集と処理を同時に行い、都市部の大気汚染の課題に対する新たな解決策となる可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://engineering.berkeley.edu/news/2023/08/scientists-develop-parallel-method-for-fog-harvesting-and-water-treatment/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41893-023-01159-9
水の採取と処理を同時に行うための光触媒反応性表面 Photocatalytically reactive surfaces for simultaneous water harvesting and treatment
Ritwick Ghosh,Adrien Baut,Giorgio Belleri,Michael Kappl,Hans-Jürgen Butt & Thomas M. Schutzius
Nature Sustainability Published:17 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-023-01159-9
Abstract
Atmospheric water harvesting provides decentralized and sustainable supplies of fresh water in areas away from natural water resources. However, an important challenge is that water sources such as fog are subject to contamination from airborne pollutants, especially near population centres. Here we demonstrate a rationally designed system that can capture fog at high efficiency while simultaneously degrading organic pollutants. At the heart of our design is a wire mesh coated with anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles embedded in a polymer matrix. Once activated by sunlight, the photoactive titanium dioxide layer decomposes organic molecules such as diesel, even in the absence of sunlight; moreover, the wettability of the mesh surface is engineered to enhance water extraction. In outdoor tests, the device can maintain a good fog harvesting performance as well as a water treatment efficiency of >85%. The continuous production of water with passive purification demonstrated in our study provides an energy-free solution to address water scarcity.