2023-06-30 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
◆従来のアクチュエーターと比べて柔軟性と環境適応性が高く、新たな「人工筋肉」の開発につながる可能性もあります。研究では、強誘電性ポリマーナノコンポジットが従来の材料の制約を克服し、性能を向上させることが示されました。しかし、課題も存在し、研究チームはそれに対する解決策も提案しています。
◆この新しい材料は、低い駆動電場でも効果的に機能するため、医療機器や光学デバイス、柔軟なロボットなど、さまざまな応用に活用できる可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/materials-research-institute/story/new-ferroelectric-material-could-give-robots-muscles/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-023-01564-7#citeas
強誘電性ポリマーナノコンポジットにおける電気熱作動性 Electro-thermal actuation in percolative ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites
Yang Liu,Yao Zhou,Hancheng Qin,Tiannan Yang,Xin Chen,Li Li,Zhubing Han,Ke Wang,Bing Zhang,Wenchang Lu,Long-Qing Chen,J. Bernholc & Qing Wang
Nature Materials Published:25 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01564-7
Abstract
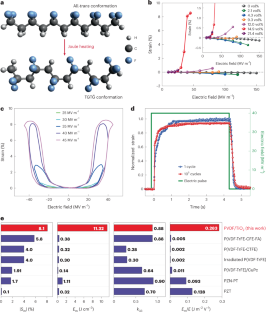
The interconversion between electrical and mechanical energies is pivotal to ferroelectrics to enable their applications in transducers, actuators and sensors. Ferroelectric polymers exhibit a giant electric-field-induced strain (>4.0%), markedly exceeding the actuation strain (≤1.7%) of piezoelectric ceramics and crystals. However, their normalized elastic energy densities remain orders of magnitude smaller than those of piezoelectric ceramics and crystals, severely limiting their practical applications in soft actuators. Here we report the use of electro-thermally induced ferroelectric phase transition in percolative ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites to achieve high strain performance in electric-field-driven actuation materials. We demonstrate a strain of over 8% and an output mechanical energy density of 11.3 J cm−3 at an electric field of 40 MV m−1 in the composite, outperforming the benchmark relaxor single-crystal ferroelectrics. This approach overcomes the trade-off between mechanical modulus and electro-strains in conventional piezoelectric polymer composites and opens up an avenue for high-performance ferroelectric actuators.