2023-02-22 アメリカ合衆国・アルゴンヌ国立研究所(ANL)
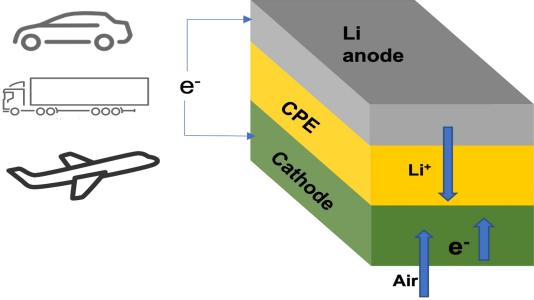
・ ANL とイリノイ工科大学が、一回の充電で 1,000 マイル(約 1,600km)の航続距離を可能にするリチウム空気電池を開発。
・ 従来設計の液体電解質に代わる固体電解質を使用した新電池設計で、リチウムイオン電池の最大 4倍のエネルギー密度(1,200Wh/kg)が可能。航空機や長距離トラックへの給電も期待できる。また、固体電解質では、液体電解質のような過熱や発火の危険性が無く、安全性が確保できる。
・ 室温下での電子 4 個による反応を初めて達成したリチウム空気電池設計で、空気中の酸素を使用して作動する。初期設計の課題であった酸素タンクも不要。
・ リチウム空気電池では、放電時にリチウム金属アノードのリチウムが液体電解質中を移動して酸素と結合後、カソードで過酸化リチウム(Li2O2)や超酸化物(LiO2)を形成し、充電時にはそれらがリチウムと酸素に分解されることでエネルギーを貯蔵・放出する。
・ 新電池設計の固体電解質は、比較的安価な元素のナノ粒子ベースのセラミックポリマー材料で構成され、放電時に酸化リチウム(Li2O)生成反応を促進する。従来の Li2O2 や LiO2 の化学反応に含まれる電子は酸素分子毎に 1~2 個。一方、Li2O では 4 個の電子が含まれるため、より高いエネルギー密度が得られる。
・ 本研究は、Joint Center for Energy Storage Research(JCESR)を通じて米国エネルギー省(DOE)の自動車技術局(VTO)と基礎エネルギー科学局(BES)が資金を提供した。
URL: https://www.anl.gov/article/new-design-for-lithiumair-battery-could-offer-much-longer-driving-range-compared-with-the-lithiumion
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
関連情報
Science 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
A room temperature rechargeable Li2O-based lithium-air battery enabled by a solid electrolyte
URL: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abq1347
An enabling composite electrolyte
Lithium-air batteries have scope to compete with gasoline in terms of energy density. However, in most systems, the reaction pathways either involve one- or two-electron transfer, leading to lithium peroxide (Li2O2) or lithium superoxide (LiO2), respectively. Kondori et al. investigated a lithium-air battery that uses a ceramic-polyethylene oxide–based composite solid electrolyte and found that it can undergo a four-electron redox reaction through lithium oxide (Li2O) formation and decomposition (see the Perspective by Dong and Lu). The composite electrolyte embedded with Li10GeP2S12 nanoparticles shows high ionic conductivity and stability and high cycle stability through a four-electron transfer process. —MSL
Abstract
A lithium-air battery based on lithium oxide (Li2O) formation can theoretically deliver an energy density that is comparable to that of gasoline. Lithium oxide formation involves a four-electron reaction that is more difficult to achieve than the one- and two-electron reaction processes that result in lithium superoxide (LiO2) and lithium peroxide (Li2O2), respectively. By using a composite polymer electrolyte based on Li10GeP2S12 nanoparticles embedded in a modified polyethylene oxide polymer matrix, we found that Li2O is the main product in a room temperature solid-state lithium-air battery. The battery is rechargeable for 1000 cycles with a low polarization gap and can operate at high rates. The four-electron reaction is enabled by a mixed ion–electron-conducting discharge product and its interface with air.