2023-04-26 オーストラリア連邦研究会議(ARC),ニューサウスウェールズ大学(UNSW)
オーストラリアのUNSW Sydneyの研究者らが、OLEDを用いて、磁気共鳴を利用して磁場をマッピングできることを示した。これは、従来の大型かつ高価な装置とは異なり、小型、柔軟性があり、量産可能であり、商業化の可能性がある。OLEDは、テレビやスマートフォンの画面に使用されることがあり、磁場に高い感度があるため、新しい技術の商業開発において魅力的な見通しを持つ。
<関連情報>
- https://excitonscience.com/news/quantum-sensing-your-pocket-using-oleds-image-magnetic-fields
- https://newsroom.unsw.edu.au/news/science-tech/material-found-smartphone-screens-can-be-harnessed-map-magnetic-fields
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37090-y
有機発光ダイオードを用いたサブミクロンスピンベース磁場イメージング Sub-micron spin-based magnetic field imaging with an organic light emitting diode
Rugang Geng,Adrian Mena,William J. Pappas & Dane R. McCamey
Nature CommunicationsPublished:15 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37090-y
Abstract
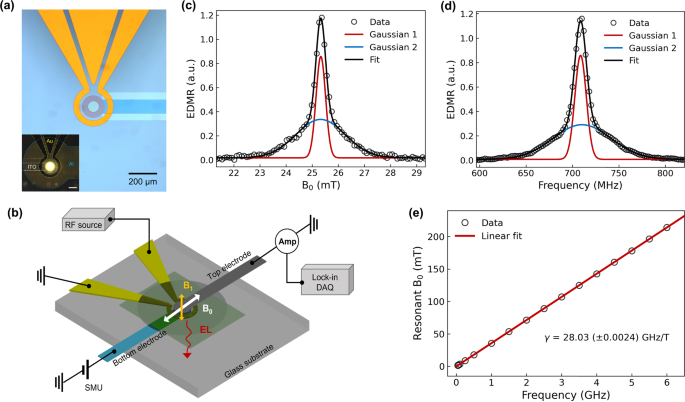
Quantum sensing and imaging of magnetic fields has attracted broad interests due to its potential for high sensitivity and spatial resolution. Common systems used for quantum sensing require either optical excitation (e.g., nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond, atomic vapor magnetometers), or cryogenic temperatures (e.g., SQUIDs, superconducting qubits), which pose challenges for chip-scale integration and commercial scalability. Here, we demonstrate an integrated organic light emitting diode (OLED) based solid-state sensor for magnetic field imaging, which employs spatially resolved magnetic resonance to provide a robust mapping of magnetic fields. By considering the monolithic OLED as an array of individual virtual sensors, we achieve sub-micron magnetic field mapping with field sensitivity of ~160 µT Hz−1/2 µm−2. Our work demonstrates a chip-scale OLED-based laser free magnetic field sensor and an approach to magnetic field mapping built on a commercially relevant and manufacturable technology.