2023-03-17 スウォンジー大学
この研究は、イタドリの管理手法の環境影響を、製品のライフサイクル全体を考慮したライフサイクルアセスメント(LCA)を用いて調査し、最も環境にやさしい方法を見つけることを目的として行われた。研究により、イタドリの管理には、使用する物質の量や経済的なコストを考慮し、生産にかかる環境影響も含めた総合的な評価が必要であることが示された。
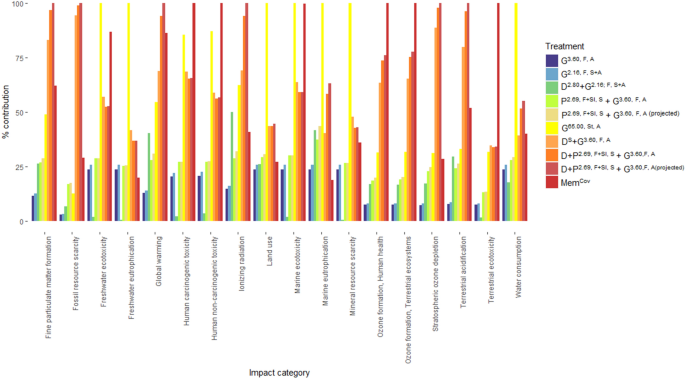
その結果、最も持続可能な手法は、物質使用量が少なく、環境に与える影響が最小限で、経済的負担も少ないグリホサートベースの葉面散布制御方法であることがわかった。
<関連情報>
- https://www.swansea.ac.uk/press-office/news-events/news/2023/03/new-study-counts-the-environmental-cost-of-managing-knotweed-.php
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-30366-9
イタドリ管理方法の相対的影響と経済コストの評価 Assessing the relative impacts and economic costs of Japanese knotweed management methods
Sophie Hocking,Trisha Toop,Daniel Jones,Ian Graham & Daniel Eastwood
Scientific Reports Published:17 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-30366-9
Abstract
Sustainable land management encompasses a range of activity that balance land use requirements with wider conservation and ecosystem impact considerations. Perennial invasive alien plants (IAPs), such as Japanese knotweed, cause severe ecological and socio-economic impacts, and methods to control their spread also come at a cost. Synthetic herbicides are generally viewed as less sustainable and more ecologically damaging than alternative approaches. Here we used a comparative Life Cycle Assessment to evaluate the sustainability of herbicide-based management approaches and physical alternatives, using a large-scale Japanese knotweed field study as a model IAP system. Glyphosate-based methods elicited the lowest environmental impacts and economic costs during production. Geomembrane covering and integrated physiochemical methods were the costliest and imposed the greatest impacts. We discuss the costs and benefits of chemical and physical approaches for the sustainable management of invaded land and question how sustainable environmental stewardship is defined for the control of IAPs.