2023-02-09 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
◆ペンシルベニア州立大学の研究チームは、新しいクラスのイオン交換膜ウェハーアセンブリを発明し、電極イオン化法の液体混合物からのp-クマル酸の捕捉能力を大幅に向上させるとともに、より少ないエネルギーとコストで電極イオン化を行うことに成功した。研究成果は、ACS Sustainable Chemical Engineering誌に掲載されました。
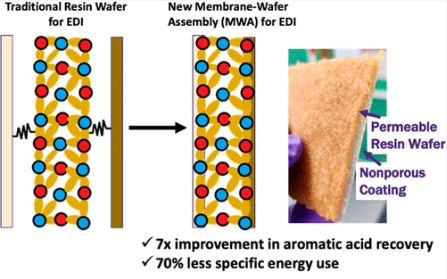
◆水の浄化に初めて実用化された電気泳動法は、近年、廃棄物から有価物を回収するために利用されています。このプロセスでは、複数のイオン交換膜と樹脂ウェーハをスポンジのように重ね、高分子接着剤で固定したものに、液体混合物を流す。電気を流すと、液体中のイオンが膜の中を移動し、p-クマル酸が濃縮されたプロセスストリームに分離され、そこで回収することができる。
◆ウェハーに膜を接着することで、必要な膜の量を30%減らし、電気陰極処理装置のコストを削減することができました。また、スポンジの上下に空隙を設けず、同じ膜とバインダーを接着することで、膜とウエハーの間の界面抵抗も低減させた。この抵抗の低減により、p-クマル酸の捕捉率が向上し、より小型のユニットを使用することが可能になりました。
◆ルイジアナ州立大学化学准教授、Kumarは、イミダゾリウムが、p-クマル酸の溶解度を高めて、材料内での拡散を促進することを発見しました。
◆透過性が高まれば、p-クマル酸が膜を通過する代わりに、ファウリングと呼ばれる膜樹脂ウエハー素材に結合する可能性が低くなる。
◆研究者によると、現行の樹脂ウェハー構成と比較した場合、新しい膜構成と材料では、p-クマル酸の捕捉率が7倍向上し、エネルギー使用量は70%減少しました。また、この新構造により、プロセスで使用する膜の量が減り、大幅なコスト削減が可能になりました。
◆アルゴンヌ国立研究所のArgesの共同研究者は、この新しい膜ウェハー組立技術の特許を申請した。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/engineering/story/researchers-use-water-treatment-method-capture-acids-agricultural-waste/
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05255
電解イオン交換法による芳香族有機酸分離のためのイオン交換樹脂製ウェハー一体型アセンブリー Integrated Ion-Exchange Membrane Resin Wafer Assemblies for Aromatic Organic Acid Separations Using Electrodeionization
Matthew L. Jordan, Grzegorz Kokoszka, Hishara Keshani Gallage Dona, Dodangodage Ishara Senadheera, Revati Kumar, Yupo J. Lin and Christopher G. Arges
ACS Sustainable Chemical Engineering Published:January 11, 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05255
Abstract
Aromatic acids, such as p-coumaric acid, are valuable chemical intermediates that are used in the specialty chemical industries because they are precursors to phenylpropanoid compounds. The separation of p-coumaric acid from fermentation broths is a critical step in the biochemical production process and more broadly the circular carbon economy. Electrodeionization (EDI) has been applied toward separations of low-carbon chain acids, but purifying p-coumaric acid has been challenging due to fouling and irreversible binding with ion-exchange membranes and resins. Here, we report a new membrane wafer assembly (MWA) consisting of laminated ion exchange membranes to porous ionomer-binder resin wafers for EDI. The MWAs in an EDI stack showed a 7-fold increase in p-coumaric acid capture while also using 70% less specific energy consumption when benchmarked against state-of-the-art resin wafer EDI modules. The more efficient p-coumaric acid recovery was ascribed to (i) the 38% reduction in interfacial transport resistance between the membrane and resin wafer and (ii) using imidazolium anion exchange membranes and ionomer binders in the MWA. MD simulations revealed enhanced transport rates for p-coumarate in imidazolium ionomers through π–π interactions. Adopting the new MWA significantly reduced the amount of ion-exchange membranes in EDI and may lead to drastic capital cost savings.


