2025-12-30 中国科学院(CAS)
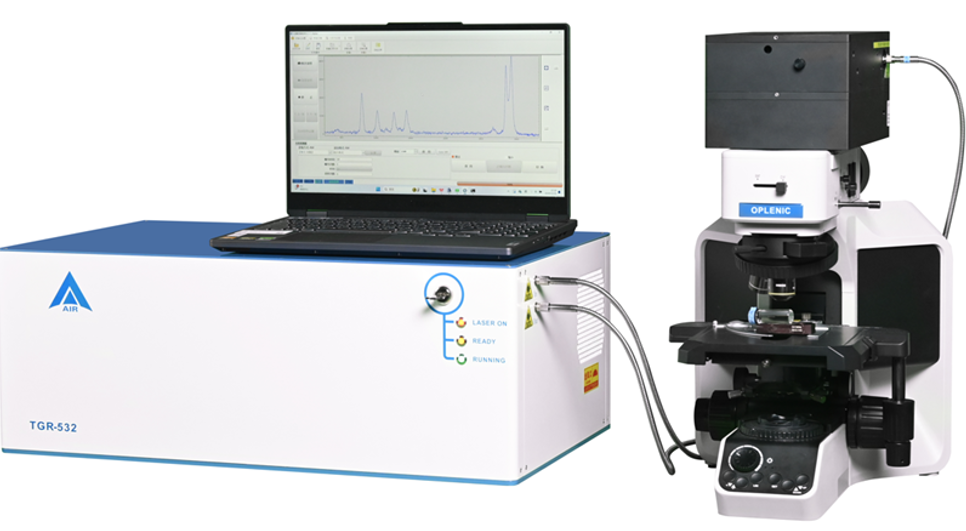 Prototype of the microscope-integrated time-gated Raman spectrometer. (Image by AIRCAS)
Prototype of the microscope-integrated time-gated Raman spectrometer. (Image by AIRCAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research-news/202602/t20260210_1150597.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.5c18910
時間ゲートラマン分光法による3,000年前の象牙の劣化経路の解明:蛍光を使わない遺産科学へのアプローチ Time-Gated Raman Spectroscopy Decodes Degradation Pathways in 3,000-Year-Old Ivories: A Fluorescence-Free Approach to Heritage Science
Jinchang Xu,Qing Xiao,Yuanyuan Niu,Xiao Zhang,Min Hu,Qingdi Sun,Haoheng Feng,Guangyou Fang,Jianbo Guo,Hui Zhang,Xiaoqiuyan Zhang,and Zhenyou Wang
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces Published: November 21, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5c18910
Abstract
Archaeological ivories are of great cultural significance but pose analytical challenges due to heterogeneous surface composition and intense fluorescence. In this study, 532 nm time-gated Raman spectroscopy was employed to overcome these limitations, enabling high spatial resolution and effective fluorescence suppression for detailed compositional analysis. Four ivory samples from Sacrificial Pits No. 3 (K3) and No. 7 (K7) exhibited markedly different preservation states. K3 samples showed evidence of copper corrosion, lower fluorescence intensity, and greater calcium loss, while K7 samples suffered from more severe sulfate-driven hydroxyapatite degradation. Sulfate substitution was found closely associated with phosphate peak broadening and surface discoloration, identifying it as a key indicator of mineral deterioration. Residual protein was detected in all specimens, with K3 samples retaining higher nitrogen content. These results demonstrate the strength of time-gated Raman spectroscopy for nondestructive, spatially resolved analysis of ancient ivory and reveal degradation pathways shaped by burial microenvironments─offering essential insights for the scientific conservation of archeological ivory.


